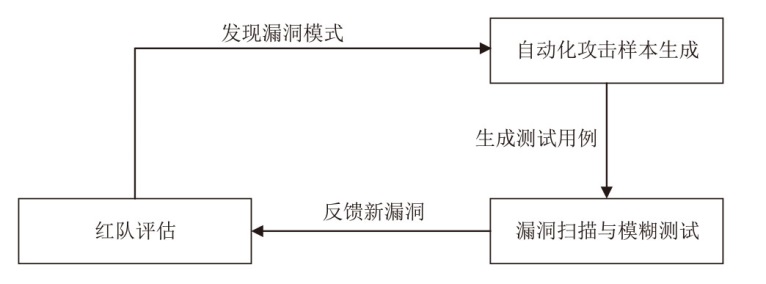
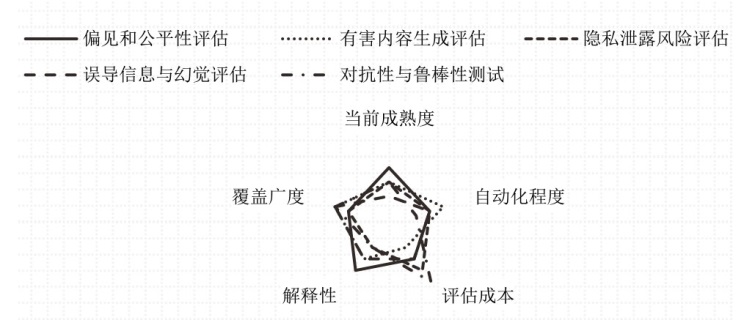
Netinfo Security ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (10): 1477-1492.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.10.001
A Review of Safety Detection and Evaluation Technologies for Large Models
HU Bin1, HEI Yiming2, WU Tiejun3, ZHENG Kaifa4,5( ), LIU Wenzhong6
), LIU Wenzhong6
- 1. College of Computer Science and Technology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2. Artificial Intelligence Research Institute, China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, Beijing 100083, China
3. School of Computer Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
4. College of Computer Science and Technology, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
5. Beijing Shenzhou NSFOCUS Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing 100089, China
6. School of Computer Science, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
-
Received:2025-06-15Online:2025-10-10Published:2025-11-07 -
Contact:ZHENG Kaifa E-mail:zhengkaifa@zju.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HU Bin, HEI Yiming, WU Tiejun, ZHENG Kaifa, LIU Wenzhong. A Review of Safety Detection and Evaluation Technologies for Large Models[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(10): 1477-1492.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://netinfo-security.org/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.10.001
| 评估方法 | 评估对象 | 技术手段 | 典型应用场景 | 核心优势 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基于上下文的评估 | 模型对不同社会/文化背景的响应差异 | 设计特定上下文探针,观察模型行为偏差 | 检测招聘对话中是否存在性别歧视倾向 | 揭示隐性偏见,反映现实情境中的公平性缺陷 |
| 基于生成文本的 评估 | 模型自由生成内容的偏见性 | 分析输出文本中的刻板印象、歧视性描述或不公平表述 | 评估故事生成中对特定群体的负面刻画 | 直接捕捉模型自发输出的有害内容 |
| 特定任务场景评估 | 模型在现实决策任务中的公平性 | 模拟应用场景,量化不同群体间的结果差异 | 测试医疗诊断模型对不同种族患者的准确性差异 | 关联实际风险,为落地部署提供可靠性依据 |
| 基于专业测试题库的评估 | 模型系统性偏见表现 | 使用结构化测试集,覆盖多维度偏见场景 | 全面检测模型在法律咨询、教育辅导中的公平性 | 标准化测评,支持跨模型横向对比 |
| 评估方法 | 核心攻击目标 | 攻击机制 | 典型场景 | 关键风险 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 成员推断攻击 | 判断特定数据点是否在训练集中 | 输入相似样本,观察模型输出置信度或行为差异 | 模型训练数据是否存在某用户病历 | 暴露数据参与情况,违反数据匿名性 |
| 数据提取攻击 | 恢复训练数据中的原始敏感信息 | 通过精心设计的提示/重复提问,诱导模型逐字输出训练数据片段 | 提取模型记忆的身份证号、银行 账号 | 直接泄露机密数据,造成实质性隐私侵害 |
| 属性推断攻击 | 推断已知训练集成员的未公开敏感属性 | 基于模型输出反推个体隐藏属性 | 推测某用户的宗教信仰或疾病史 | 侵犯个人隐私,导致歧视或勒索风险 |
| 训练数据记忆风险评估 | 评估模型对敏感信息的记忆强度 | 构造含敏感模式的查询,检测模型是否泄露关联信息 | 检测模型是否记忆罕见医疗记录或专利文本 | 揭示模型记忆偏好,量化敏感数据暴露 概率 |
| 评估方法 | 核心机制 | 适用场景 | 关键优势 | 主要局限 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基于事实的核查 | 比对模型生成内容与权威知识库/信息源,验证真实性 | 历史事件、科学事实等描述的准确性检测 | 直接验证内容真实性,依赖权威来源 | 依赖知识库覆盖范围,无法检测逻辑矛盾 |
| 基于一致性的评估 | 通过不同提问方式测试回答的一致性 | 科学定律、概念解释等多角度提问场景 | 揭示模型内在矛盾,评估输出稳定性 | 不直接验证事实,仅反映逻辑一致性 |
| 多模态鲁棒性基准 | 设计正/负向问题测试模型对误导性信息的抵抗能力 | 多模态大模型 (文本+图像/视频) | 量化模型抗干扰能力,专为多模态场景设计 | 需定制测试集,泛化性依赖基准质量 |
| 检索增强生成系统评估 | 联合评估生成内容质量 + 检索信息的准确性、相关性 | 检索增强生成(RAG)系统[ | 确保外部知识有效整合,提升结果可解释性 | 需多模块协同评估,复杂 度高 |
| 人类评估 | 评估员基于专业知识分析内容,识别幻觉/误导 | 需深度语义理解的复杂场景 | 提供主观洞察,发现自动化方法遗漏的细微错误 | 成本高、可扩展性差,存在主观偏差 |
| [1] |
YAO Yifan, DUAN Jinhao, XU Kaidi, et al. A Survey on Large Language Model (LLM) Security and Privacy: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly[J]. High-Confidence Computing, 2024, 4(2): 100211-100233.
doi: 10.1016/j.hcc.2024.100211 URL |
| [2] | WANG Qiaochen, WU Zhengang, LIU Hu. Overview of Security and Privacy Issues in the Application of Large Language Models[J]. Industrial Information Security, 2024(5): 40-45. |
| 王乔晨, 吴振刚, 刘虎. 大语言模型应用的安全与隐私问题综述[J]. 工业信息安全, 2024(5): 40-45. | |
| [3] | HOU Chao, MIAO Haoyu, BAO Tianyuan, et al. A Brief Discussion on the Application of Large Models in Cybersecurity[J]. Network Security and Informatization, 2025(3): 1-3. |
| 侯超, 苗浩宇, 鲍天远, 等. 浅谈大模型在网络安全中的应用[J]. 网络安全和信息化, 2025(3): 1-3. | |
| [4] |
TIMPERLEY R L, BERTHOUD L, SNIDER C, et al. Assessment of Large Language Models for Use in Generative Design of Model Based Spacecraft System Architectures[J]. Journal of Engineering Design, 2025, 36(4): 550-570.
doi: 10.1080/09544828.2025.2453401 URL |
| [5] | TAI Jianwei, YANG Shuangning, WANG Jiajia, et al. Survey of Adversarial Attacks and Defenses for Large Language Models[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2025, 62(3): 563-588. |
| 台建玮, 杨双宁, 王佳佳, 等. 大语言模型对抗性攻击与防御综述[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2025, 62(3): 563-588. | |
| [6] |
ZHANG Ran, LI Hongwei, QIAN Xinyuan, et al. On Large Language Models Safety, Security, and Privacy: A Survey[J]. Journal of Electronic Science and Technology, 2025, 23(1): 100301-100311.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnlest.2025.100301 URL |
| [7] | ETSI. Aqua Security Listed in OWASP’s LLM and Generative AI Security Solutions Landscape Guide for 2025[J]. Manufacturing Close-Up, 2024(12): 1-7. |
| [8] | KUANG Hongyu. Research on Key Technologies for Software Vulnerability Detection Based on Pre-Trained Language Models[D]. Beijing: Academy of Military Sciences, 2024. |
| 匡洪宇. 基于预训练语言模型的软件漏洞检测关键技术研究[D]. 北京: 军事科学院, 2024. | |
| [9] | LI Jihong, YU Yanfang, YU Qiwei, et al. Chinese Open Relation Extraction Based on Large Language Model and Multi-Dimensional Self-Reflective Learning[EB/OL]. (2025-05-30)[2025-06-01]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/10.1478.G2.20250530.1140.002.html. |
| 李翼鸿, 余燕芳, 余奇伟, 等. 基于大语言模型与多维度自我反思学习的中文开放关系抽取[EB/OL]. (2025-05-30)[2025-06-01]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/10.1478.G2.20250530.1140.002.html. | |
| [10] | YANG Jirui, LIN Zheyu, YANG Shuhan, et al. Concept Enhancement Engineering: A Lightweight and Efficient Robust Defense against Jailbreak Attacks in Embodied AI[EB/OL]. (2025-04-15)[2025-06-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.13201. |
| [11] | SHI Dan, SHEN Tianhao, HUANG Yufei, et al. Large Language Model Safety: A Holistic Survey[EB/OL]. (2024-12-23)[2025-06-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.17686. |
| [12] | ANDERSON S C, SUMMERS D, OUYANG M, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Low-Intensity Versus Standard Monitoring Following Intravenous Thrombolytic Treatment in Patients with Acute Ischaemic Stroke (OPTIMISTmain): An International, Pragmatic, Stepped-Wedge, Cluster-Randomised, Controlled Non-Inferiority Trial[J]. The Lancet, 2025, 4(5): 1909-1922. |
| [13] | WANG Kun, ZHANG Guibin, ZHOU Zhenhong, et al. A Comprehensive Survey in LLM(Agent) Full Stack Safety: Data, Training and Deployment[EB/OL]. (2025-04-22)[2025-06-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.15585. |
| [14] | NI Bo, LIU Zheyuan, WANG Leyao, et al. Towards Trustworthy Retrieval Augmented Generation for Large Language Models: A Survey[EB/OL]. (2025-02-08)[2025-06-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.06872. |
| [15] | ZHANG Xuewang, LU Hui, XIE Haofei. A Data Augmentation Method Based on Graph Node Centrality and Large Model for Vulnerability Detection[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(4): 550-563. |
| 张学旺, 卢荟, 谢昊飞. 基于节点中心性和大模型的漏洞检测数据增强方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(4): 550-563. | |
| [16] | GUO Xiangxin, LIN Jingqiang, JIA Shijie, et al. Security Analysis of Cryptographic Application Code Generated by Large Language Model[J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(6): 917-925. |
| 郭祥鑫, 林璟锵, 贾世杰, 等. 针对大语言模型生成的密码应用代码安全性分析[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(6): 917-925. | |
| [17] |
BEVARA K V R, MANNURU R N, KAREDLA P S, et al. Scaling Implicit Bias Analysis across Transformer-Based Language Models through Embedding Association Test and Prompt Engineering[J]. Applied Sciences, 2024, 14(8): 3483-3492.
doi: 10.3390/app14083483 URL |
| [18] | QU Youzhi, WEI Chen, DU Penghui, et al. Integration of Cognitive Tasks into Artificial General Intelligence Test for Large Models[J]. IScience, 2024, 27(4): 50-59. |
| [19] |
KURUMAYYA V. Towards Fair AI: A Review of Bias and Fairness in Machine Intelligence[J]. Journal of Computational Social Science, 2025, 8(3): 55-65.
doi: 10.1007/s42001-025-00386-8 |
| [20] | SONG Jialei, ZUO Xingquan, ZHANG Xiujian, et al. Overview of Evaluation Methods for Large Language Models[J]. Aerospace Measurement Technology, 2025, 45(2): 1-30. |
| 宋佳磊, 左兴权, 张修建, 等. 大语言模型评估方法综述[J]. 宇航计测技术, 2025, 45(2): 1-30. | |
| [21] |
RAVINDRANATH R, STEIN D J, BOUSSARD H T, et al. The Impact of Race, Ethnicity, and Sex on Fairness in Artificial Intelligence for Glaucoma Prediction Models[J]. Ophthalmology Science, 2025, 5(1): 100596-100608.
doi: 10.1016/j.xops.2024.100596 URL |
| [22] |
BROWN E K, YAN Chao, LI Zhuohang, et al. Large Language Models Are Less Effective at Clinical Prediction Tasks than Locally Trained Machine Learning Models[J]. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association: JAMIA, 2025, 32(5): 811-822.
doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocaf038 URL |
| [23] | CHEN Haoling, LIU Peng. Stock Return Prediction Using Financial News: A Unified Sequence Model Based on Hierarchical Attention and Long-Short Term Memory Networks[C]// IEEE. International Conference on Signal Processing and Machine Learning (CONF-SPML 2021). New York: IEEE, 2021: 147-152. |
| [24] | ZHANG Zhanfeng, MA Hongfeng, JIANG Xin. Overview of Bias Assessment and Correction for Pre-Trained Language Models[EB/OL]. (2025-05-22)[2025-06-01]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1671.TP.20250521.1617.014.html. |
| 张展峰, 马宏伟, 姜鑫. 预训练语言模型的偏见评估与纠正综述[EB/OL]. (2025-05-22)[2025-06-01]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1671.TP.20250521.1617.014.html. | |
| [25] |
PARDHI P. Content Moderation of Generative AI Prompts[J]. SN Computer Science, 2025, 6(4): 329-336.
doi: 10.1007/s42979-025-03864-y |
| [26] |
AGHA S D M, WAZZAN A A F. Evaluating the Impact of Gypsum Content on the Physical and Hydraulic Properties of Soils in Arid Regions: A Review[J]. Asian Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2025, 11(1): 217-225.
doi: 10.9734/ajsspn/2025/v11i1475 URL |
| [27] | XU Zhiwei, LI Hailong, LI Bo, et al. Overview of AIGC Large Model Evaluation: Enabling Technologies, Security Risks, and Countermeasures[J]. Computer Science and Exploration, 2024, 18(9):2293-2325. |
|
许志伟, 李海龙, 李博, 等. AIGC大模型测评综述:使能技术、安全隐患和应对[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2024, 18(9): 2293-2325.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2402023 |
|
| [28] | XIE Yueqi, FANG Minghong, PI Renjie, et al. GradSafe: Detecting Jailbreak Prompts for LLMs via Safety-Critical Gradient Analysis[EB/OL]. (2024-12-21)[2025-06-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.13494. |
| [29] | LI Jie, LI Zhengfang, ZOU Yao, et al. Evaluation Method for Multi-Language Word Alignment Capability of Large Language Models[J]. Journal of Southwest Minzu University (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 50(6): 681-688. |
| 李洁, 李正芳, 邹垚, 等. 大语言模型多语言词对齐能力评测方法[J]. 西南民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 50(6): 681-688. | |
| [30] | XIE Lixia, SHI Jingchen, YANG Hongyu, et al. Member Inference Attack Based on Graph Neural Network Model Calibration[J]. Journal of Electronics and Information Technology, 2025, 47(3): 780-791. |
| 谢丽霞, 史镜琛, 杨宏宇, 等. 基于图神经网络模型校准的成员推理攻击[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(3): 780-791. | |
| [31] | CUI Qimei, YOU Xiaohu, WEI Ni, et al. Overview of AI and Communication for 6G Network: Fundamentals, Challenges, and Future Research Opportunities[EB/OL]. (2025-04-03)[2025-06-01]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.5847.TP.20250403.1018.008.html. |
| [32] | HAN Zhen, ZHOU Wen’an, HAN Xiaoxuan, et al. Black-Box Membership Inference Attacks Based on Shadow Model[J]. The Journal of China Universities of Posts and Telecommunications, 2024, 31(4): 1-16. |
| [33] |
RAN Lingqin, PENG Changgen, XU Dequan, et al. Privacy Leakage Risk Assessment Method Based on Blockchain Technology Architecture[J]. Computer Engineering, 2023, 49(1): 146-153.
doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0063637 |
|
冉玲琴, 彭长根, 许德权, 等. 基于区块链技术架构的隐私泄露风险评估方法[J]. 计算机工程, 2023, 49(1): 146-153.
doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0063637 |
|
| [34] | ZHOU Xin, WEYSSOW M, WIDYASARI R, et al. LessLeak-Bench: A First Investigation of Data Leakage in LLMs across 83 Software Engineering Benchmarks[EB/OL]. (2025-02-10)[2025-06-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.06215. |
| [35] | DING Jie. Research on Identifying Fake News about Epidemics Based on Deep Learning[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Gongshang University, 2023. |
| 丁杰. 基于深度学习的信息疫情假新闻甄别研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工商大学, 2023. | |
| [36] | MENG Jiachun, FANG Jing, ZHOU Ziqi, et al. Vehicle Collision Sound Recognition Method Based on Convolutional Neural Network[EB/OL]. (2025-05-27)[2025-06-01]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2121.O4.20250527.0813.002.html. |
| 孟家醇, 方靖, 周子奇, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的车辆碰撞声识别方法[EB/OL]. (2025-05-27)[2025-06-01]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2121.O4.20250527.0813.002.html. | |
| [37] | SUN Jin, HU Zhiyu. Follow-Up on Antitrust Regulation of Generative Artificial Intelligence under Open-Source Model[EB/OL]. (2025-05-29)[2025-06-01]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/61.1352.C.20250528.2203.004.html. |
| 孙晋, 胡旨钰. 开源模式下生成式人工智能的反垄断监管跟进[EB/OL]. (2025-05-29)[2025-06-01]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/61.1352.C.20250528.2203.004.html. | |
| [38] | GUAN Tianrui, LIU Fuxiao, WU Xiyang, et al. HallusionBench: An Advanced Diagnostic Suite for Entangled Language Hallucination and Visual Illusion in Large Vision-Language Models[EB/OL]. (2023-02-23)[2025-06-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.14566. |
| [39] | DU Yanrui, ZHAO Sendong, ZHAO Danyang, et al. MoGU: A Framework for Enhancing Safety of Open-Sourced LLMs While Preserving Their Usability[EB/OL]. (2024-05-23)[2025-06-01]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2405.14488. |
| [40] | HAZRA R, LAYEK S, BANERJEE S, et al. Safety Arithmetic: A Framework for Test-Time Safety Alignment of Language Models by Steering Parameters and Activations[EB/OL]. (2024-07-17)[2025-06-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.11801. |
| [41] | YI Xin, ZHENG Shunfan, WANG Linlin, et al. NLSR: Neuron-Level Safety Realignment of Large Language Models against Harmful Fine-Tuning[EB/OL]. (2024-12-17)[2025-06-01]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2412.12497v1. |
| [42] |
HAIDER Z, RAHMAN H M, DEVABHAKTUNI V, et al. A Framework for Mitigating Malicious RLHF Feedback in LLM Training Using Consensus Based Reward[J]. Scientific Reports, 2025, 15(1): 9177-9184.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92889-7 |
| [43] | WANG Jie, WANG Zitong, PENG Yan, et al. Research on the Prediction of Popularity of Multimodal Social Media Information Based on Large Language Models[J]. Journal of Communications, 2024, 45(11): 141-156. |
|
王洁, 王子曈, 彭岩, 等. 基于大语言模型的多模态社交媒体信息流行度预测研究[J]. 通信学报, 2024, 45(11): 141-156.
doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2024193 |
|
| [44] |
ZHAO Liang. TS-HTFA: Advancing Time-Series Forecasting via Hierarchical Text-Free Alignment with Large Language Models[J]. Symmetry, 2025, 17(3): 401-410.
doi: 10.3390/sym17030401 URL |
| [45] | ZHANG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Cen, LI Tianlin, et al. JailGuard: A Universal Detection Framework for LLM Prompt-Based Attacks[EB/OL]. (2023-12-17)[2025-06-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.10766. |
| [46] |
XIANG Yawen, ZHOU Heng, LI Chengyang, et al. Deep Learning in Motion Deblurring: Current Status, Benchmarks and Future Prospects[J]. The Visual Computer, 2024, 41(6): 1-27.
doi: 10.1007/s00371-024-03766-9 |
| [47] | YANG Hong, WU Jun, GUAN Xinping. A Survey of Joint Security-Safety for Function, Information and Human in Industry 5.0[J]. Security and Safety, 2025, 4(1): 56-106. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||