Netinfo Security ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (10): 1554-1569.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.10.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
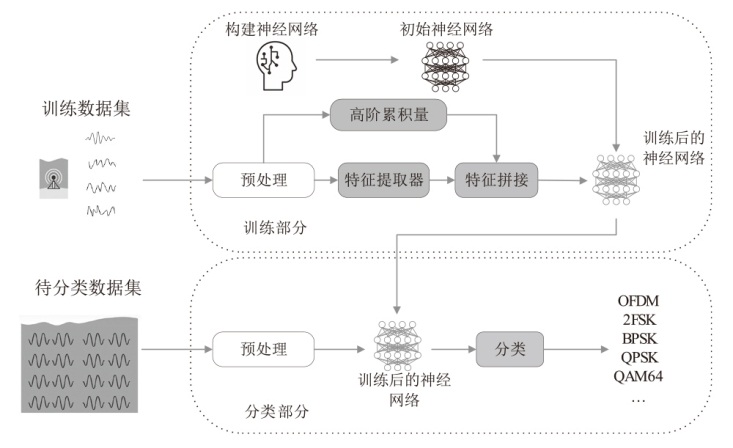
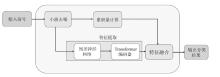
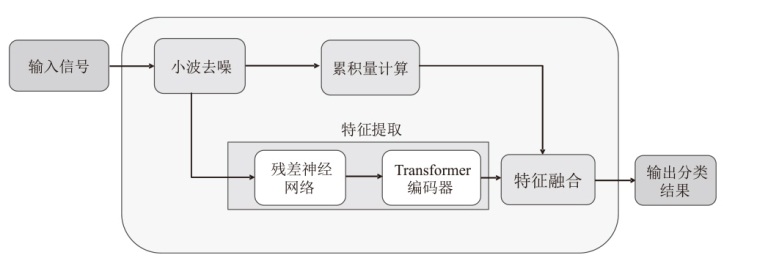
A Cumulant-Deep Learning Fusion Model for Underwater Modulation Recognition
LI Guyue1,2, ZHANG Zihao1( ), MAO Chenghai1, LYU Rui1
), MAO Chenghai1, LYU Rui1
- 1. School of Cyber Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing 211189, China
2. Purple Mountain Laboratories for Network Communication and Security, Nanjing 211111, China
-
Received:2025-07-02Online:2025-10-10Published:2025-11-07 -
Contact:ZHANG Zihao E-mail:220235436@seu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LI Guyue, ZHANG Zihao, MAO Chenghai, LYU Rui. A Cumulant-Deep Learning Fusion Model for Underwater Modulation Recognition[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(10): 1554-1569.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://netinfo-security.org/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.10.007
| [1] |
SONG Aijun, STOJANOVIC M, CHITRE M. Editorial Underwater Acoustic Communications: Where We Stand and What is Next?[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2019, 44(1): 1-6.
doi: 10.1109/JOE.2018.2883872 |
| [2] | JIANG Shengming. On Securing Underwater Acoustic Networks: A Survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 21(1): 729-752. |
| [3] | JIANG Shengming. On Reliable Data Transfer in Underwater Acoustic Networks: A Survey from Networking Perspective[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(2): 1036-1055. |
| [4] |
HUANG Jianchun, DIAMANT R. Adaptive Modulation for Long-Range Underwater Acoustic Communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(10): 6844-6857.
doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3006230 URL |
| [5] |
ALI M F, JAYAKODY D N K, CHURSIN Y A, et al. Recent Advances and Future Directions on Underwater Wireless Communications[J]. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2020, 27(5): 1379-1412.
doi: 10.1007/s11831-019-09354-8 |
| [6] | GHOREYSHI S M, SHAHRABI A, BOUTALEB T. Void-Handling Techniques for Routing Protocols in Underwater Sensor Networks: Survey and Challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(2): 800-827. |
| [7] | ZHAO Caidan, CHEN Jingqian, WU Zhiqiang. Automatic Modulation Recognition Algorithm Based on Multi-Channel Joint Learning[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(4): 20-29. |
| 赵彩丹, 陈璟乾, 吴志强. 基于多通道联合学习的自动调制识别网络[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(4):20-29. | |
| [8] |
XU J L, SU Wei, ZHOU Mengchu, Likelihood-Ratio Approaches to Automatic Modulation Classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews), 2010, 41(4): 455-469.
doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2010.2076347 URL |
| [9] | LI Yuxing, TANG Bingzhao, JIAO Shangbin. SO-Slope Entropy Coupled with SVMD: A Novel Adaptive Feature Extraction Method for Ship-Radiated Noise[EB/OL]. (2023-05-01)[2025-06-30]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.114677. |
| [10] | MENG Qingxin, YANG Shie. A Wave Structure Based Method for Recognition of Marine Acoustic Target Signals[EB/OL]. (2015-04-01)[2025-06-30]. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.4920186. |
| [11] |
ZHU Daimei, MATHEWS V J, DETIENNE D H. A Likelihood-Based Algorithm for Blind Identification of QAM and PSK Signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(5): 3417-3430.
doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2811802 URL |
| [12] | HONG Feng, LIU Chengwei, GUO Lijuan, et al. Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition with Resnet18 on Shipsear Dataset[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE 4th International Conference on Electronics Technology (ICET). New York: IEEE, 2021: 1240-1244. |
| [13] | JIANG Zenghui, ZENG Weijun, CHEN Pu, et al. Review of Adversarial Samples for Modulation Recognition[J]. Netinfo Security, 2023, 23(6): 74-90. |
| 蒋曾辉, 曾维军, 陈璞, 等. 面向调制识别的对抗样本研究综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(6):74-90. | |
| [14] | WANG Yan, ZHANG Hao, SANG Zhanliang, et al. Modulation Classification of Underwater Communication with Deep Learning Network[EB/OL]. (2019-04-01)[2025-06-30]. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31065254/. |
| [15] | HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition[C]// IEEE. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2016: 770-778. |
| [16] | TIAN Xiao, CHEN Chao. Modulation Pattern Recognition Based on Resnet50 Neural Network[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Information Communication and Signal Processing (ICICSP). New York: IEEE, 2019: 34-38. |
| [17] | VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is All You Need[EB/OL]. (2017-09-02)[2025-06-30]. https://papers.nips.cc/paper/2017/file/3f5ee243547dee91fbd053c1c4a845aa-Paper.pdf. |
| [18] |
CAI Jingjing, GAN Fengming, CAO Xianghai, et al. Signal Modulation Classification Based on the Transformer Network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2022, 8(3): 1348-1357.
doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2022.3176640 URL |
| [19] | LI Bing, CUI Wei, WANG Wei, et al. Two-Stream Convolution Augmented Transformer for Human Activity Recognition[C]// AAAI. The AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Menlo Park: AAAI, 2021: 286-293. |
| [20] | ZHANG Rui, YIN Zhendong, WU Zhilu, et al. A Novel Automatic Modulation Classification Method Using Attention Mechanism and Hybrid Parallel Neural Network[EB/OL]. (2021-01-02)[2025-06-30]. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11031327. |
| [21] | YU Yang, CAO Xu, ZHANG Xiaomin. Underwater Target Classification Using Deep Neural Network[C]// IEEE. 2018 Oceans-Mts/IEEE Kobe Techno-Oceans (Oto). New York: IEEE, 2018: 1-5. |
| [22] | STOJANOVIC M, PREISIG J. Underwater Acoustic Communication Channels: Propagation Models and Statistical Characterization[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2009, 47(1): 84-89. |
| [23] | CAO Xu, ZHANG Xiaomin, YU Yang, et al. Deep Learning-Based Recognition of Underwater Target[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP). New York: IEEE, 2016: 89-93. |
| [24] |
PENG Shengliang, SUN Shujun, YAO Yudong. A Survey of Modulation Classification Using Deep Learning: Signal Representation and Data Preprocessing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 33(12): 7020-7038.
doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3085433 URL |
| [25] |
CHANG Shuo, HUANG Sai, ZHANG Ruiyun, et al. Multitask-Learning-Based Deep Neural Network for Automatic Modulation Classification[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 9(3): 2192-2206.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3091523 URL |
| [26] |
PENG Shengliang, JIANG Hanyu, WANG Huaxia, et al. Modulation Classification Based on Signal Constellation Diagrams and Deep Learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 30(3): 718-727.
doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2850703 URL |
| [27] |
ZHANG Zufan, LUO Hao, WANG Chun, et al. Automatic Modulation Classification Using CNN-LSTM Based Dual-Stream Structure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(11): 13521-13531.
doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3030018 |
| [28] |
KE Ziqi, VIKALO H. Real-Time Radio Technology and Modulation Classification via an LSTM Auto-Encoder[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 21(1): 370-382.
doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3095855 URL |
| [29] |
GHASEMZADEH P, HEMPEL M, SHARIF H. GS-QRNN: A High-Efficiency Automatic Modulation Classifier for Cognitive Radio IoT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(12): 9467-9477.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3141032 URL |
| [30] |
XU Jialang, LUO Chunbo, PARR G, et al. A Spatiotemporal Multi-Channel Learning Framework for Automatic Modulation Recognition[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(10): 1629-1632.
doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2999453 |
| [31] | YUE Zhou, WEI Kong, QING Xu. A Novel Modeling and Recognition Method for Underwater Sound Based on HMT in Wavelet Domain[C]// Springer. Australasian Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Heidelberg: Springer, 2004: 332-343. |
| [32] | SAFI S, FRIKEL M, ZEROUAL A, et al. Higher Order Cumulants for Identification and Equalization of Multicarrier Spreading Spectrum Systems[J]. Journal of Telecommunications and Information Technology, 2011 (2): 74-84. |
| [33] |
ZHANG Ruoyun, CHANG Shuo, WEI Zhiqing, et al. Modulation Classification of Active Attacks in Internet of Things: Lightweight MCBLDN with Spatial Transformer Network[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(19): 19132-19146.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3163892 URL |
| [34] |
LIANG Zhi, TAO Mingliang, XIE Jian, et al. A Radio Signal Recognition Approach Based on Complex-Valued CNN and Self-Attention Mechanism[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2022, 8(3): 1358-1373.
doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2022.3179450 URL |
| [35] |
ZHANG Weilong, YANG Xinghai, LENG Changli, et al. Modulation Recognition of Underwater Acoustic Signals Using Deep Hybrid Neural Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(8): 5977-5988.
doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3144608 URL |
| [36] |
LI Juan, JIA Qingning, CUI Xuerong, et al. Automatic Modulation Recognition of Underwater Acoustic Signals Using a Two-Stream Transformer[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(10): 18839-18851.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3367852 URL |
| [1] | XU Ruzhi, WU Xiaoxin, LYU Changran. Research on Transformer-Based Super-Resolution Network Adversarial Sample Defense Method [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(9): 1367-1376. |
| [2] | CHEN Yonghao, CAI Manchun, ZHANG Yiwen, PENG Shufan, YAO Lifeng, ZHU Yi. A Multi-Scale and Multi-Level Feature Fusion Approach for Deepfake Face Detection [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(9): 1456-1464. |
| [3] | WANG Xinmeng, CHEN Junbao, YANG Yitao, LI Wenjin, GU Dujuan. Bayesian Optimized DAE-MLP Malicious Traffic Identification Model [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(9): 1465-1472. |
| [4] | JIN Zhigang, LI Zimeng, CHEN Xuyang, LIU Zepei. Review of Network Intrusion Detection System for Unbalanced Data [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(8): 1240-1253. |
| [5] | WANG Gang, GAO Yunpeng, YANG Songru, SUN Litao, LIU Naiwei. A Survey on Deep Learning-Based Encrypted Malicious Traffic Detection Methods [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(8): 1276-1301. |
| [6] | ZHANG Xinglan, TAO Kejin. Universal Perturbations Generation Method Based on High-Level Features and Important Channels [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(5): 767-777. |
| [7] | LI Jingyou, XI Xiaotian, WEI Rongle, ZHANG Guangda. Double Branch Neural Network Watermarking Algorithm Based on Wavelet Decomposition and Dynamic Dense Dilated Convolution [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(5): 828-839. |
| [8] | JIN Zengwang, JIANG Lingyang, DING Junyi, ZHANG Huixiang, ZHAO Bo, FANG Pengfei. A Review of Research on Industrial Control System Security [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(3): 341-363. |
| [9] | CHEN Hongsong, LIU Xinrui, TAO Zimei, WANG Zhiheng. A Survey of Anomaly Detection Model for Time Series Data Based on Deep Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(3): 364-391. |
| [10] | LI Hailong, CUI Zhian, SHEN Xieyang. Overview of Anomaly Analysis and Detection Methods for Network Traffic [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 194-214. |
| [11] | WU Haoying, CHEN Jie, LIU Jun. Improved Neural Network Differential Distinguisher of Simon32/64 and Simeck32/64 [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 249-259. |
| [12] | JIN Di, REN Hao, TANG Rui, CHEN Xingshu, WANG Haizhou. Research on Offensive Language Detection in Social Networks Based on Emotion-Assisted Multi-Task Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 281-294. |
| [13] | LIANG Fengmei, PAN Zhenghao, LIU Ajian. A Joint Detection Method for Physical and Digital Face Attacks Based on Common Forgery Clue Awareness [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(10): 1604-1614. |
| [14] | CHEN Xiaojing, TAO Yang, WU Baiqi, DIAO Yunfeng. Optimization Gradient Perception Adversarial Attack for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(9): 1386-1395. |
| [15] | XU Ruzhi, ZHANG Ning, LI Min, LI Zixuan. Research on a High Robust Detection Model for Malicious Software [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(8): 1184-1195. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||