Netinfo Security ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (9): 1367-1376.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.09.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research on Transformer-Based Super-Resolution Network Adversarial Sample Defense Method
XU Ruzhi, WU Xiaoxin( ), LYU Changran
), LYU Changran
- School of Control and Computer Engineering, North China Electric Power University, Beijing 102206, China
-
Received:2024-12-09Online:2025-09-10Published:2025-09-18
CLC Number:
Cite this article
XU Ruzhi, WU Xiaoxin, LYU Changran. Research on Transformer-Based Super-Resolution Network Adversarial Sample Defense Method[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(9): 1367-1376.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://netinfo-security.org/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.09.005
| 网络 模型 | 良性样本 | FGSM-2 | FGSM-10 | I-FGSM | MI-FGSM | PGD | L-BFGS | C&W | JSMA | DeepFool | ZOO | DI2FGSM | MDI2FGSM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无防御方法 | |||||||||||||
| Inc-v3 | 100.0% | 31.7% | 30.5% | 11.4% | 1.7% | 1.1% | 0.3% | 0.8% | 0.8% | 0.4% | 1.0% | 1.4% | 0.6% |
| Res-50 | 100.0% | 12.2% | 6.1% | 3.4% | 0.4% | 0.2% | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.2% | 1.0% | 0.8% | 0.3% | 0.2% |
| IncRes-v2 | 100.0% | 59.4% | 53.6% | 21.6% | 0.5% | 0.3% | 0.1% | 0.3% | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.8% | 1.5% | 0.6% |
| JPEG 压缩 | |||||||||||||
| Inc-v3 | 96.0% | 62.3% | 48.8% | 77.5% | 69.4% | 68.1% | 76.5% | 80.5% | 78.8% | 81.2% | 80.2% | 2.1% | 1.3% |
| Res-50 | 92.8% | 57.6% | 42.9% | 74.8% | 70.8% | 65.3% | 77.9% | 81.3% | 76.3% | 77.3% | 76.9% | 0.7% | 0.4% |
| IncRes-v2 | 95.5% | 67.0% | 53.7% | 81.3% | 72.8% | 66.2% | 79.4% | 83.1% | 81.6% | 83.9% | 82.9% | 1.6% | 1.1% |
| R&P | |||||||||||||
| Inc-v3 | 97.3% | 69.2% | 53.2% | 90.6% | 89.5% | 88.5% | 89.1% | 89.5% | 88.2% | 88.9% | 87.3% | 7.0% | 5.8% |
| Res-50 | 92.5% | 66.8% | 48.8% | 88.2% | 88.0% | 87.2% | 86.6% | 87.5% | 86.3% | 90.9% | 88.9% | 6.6% | 4.2% |
| IncRes-v2 | 98.7% | 70.7% | 55.8% | 87.5% | 88.3% | 86.8% | 85.1% | 88.0% | 85.6% | 89.7% | 87.9% | 7.5% | 5.3% |
| TVM+ Image Quilting | |||||||||||||
| Inc-v3 | 96.2% | 70.2% | 54.6% | 85.7% | 84.5% | 83.6% | 84.3% | 85.3% | 84.2% | 85.9% | 84.3% | 4.1% | 1.7% |
| Res-50 | 93.1% | 69.7% | 53.3% | 85.4% | 83.8% | 83.9% | 83.2% | 84.6% | 83.3% | 85.0% | 83.2% | 3.6% | 1.1% |
| IncRes-v2 | 95.6% | 74.6% | 59.0% | 86.5% | 84.8% | 82.6% | 84.3% | 85.3% | 84.1% | 86.2% | 85.9% | 4.5% | 1.2% |
| Pixel Deflection | |||||||||||||
| Inc-v3 | 91.9% | 71.1% | 58.9% | 90.9% | 90.1% | 90.0% | 90.2% | 90.4% | 87.9% | 88.1% | 87.1% | 57.6% | 21.9% |
| Res-50 | 92.7% | 84.6% | 66.8% | 91.2% | 89.6% | 88.5% | 89.9% | 91.7% | 88.6% | 90.3% | 89.9% | 57.0% | 29.5% |
| IncRes-v2 | 92. 1% | 78.2% | 71.6% | 91.3% | 89.8% | 89.2% | 88.4% | 89.7% | 86.1% | 88.9% | 86.2% | 57.9% | 24.6% |
| SR-ResNet | |||||||||||||
| Inc-v3 | 94.0% | 89.5% | 69.9% | 93.4% | 92.6% | 91.5% | 92.1% | 93.3% | 90.4% | 93.2% | 90.8% | 54.3% | 24.9% |
| Res-50 | 92.8% | 85.5% | 62.3% | 90.8% | 90.6% | 91.1% | 90.8% | 92.1% | 89.9% | 90.5% | 89.8% | 60.1% | 29.8% |
| IncRes-v2 | 95.2% | 92.6% | 79.9% | 94.2% | 93.1% | 92.9% | 93.5% | 94.2% | 92.3% | 94.1% | 94.3% | 65.2% | 36.6% |
| 小波去噪+EDSR | |||||||||||||
| Inc-v3 | 97.0% | 94.2% | 79.7% | 96.2% | 95.9% | 95.1% | 95.2% | 96.0% | 95.1% | 96.1% | 95.6% | 67.9% | 31.7% |
| Res-50 | 93.9% | 86.1% | 64.9% | 92.3% | 92.0% | 92.3% | 92.6% | 93.1% | 92.1% | 91.5% | 90.1% | 60.7% | 31.9% |
| IncRes-v2 | 98.2% | 95.3% | 82.3% | 95.8% | 95.0% | 94.3% | 95.6% | 95.6% | 94.8% | 96.0% | 95.7% | 69.8% | 35.6% |
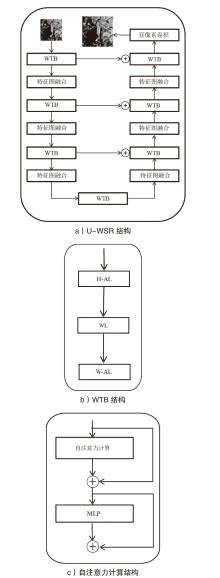
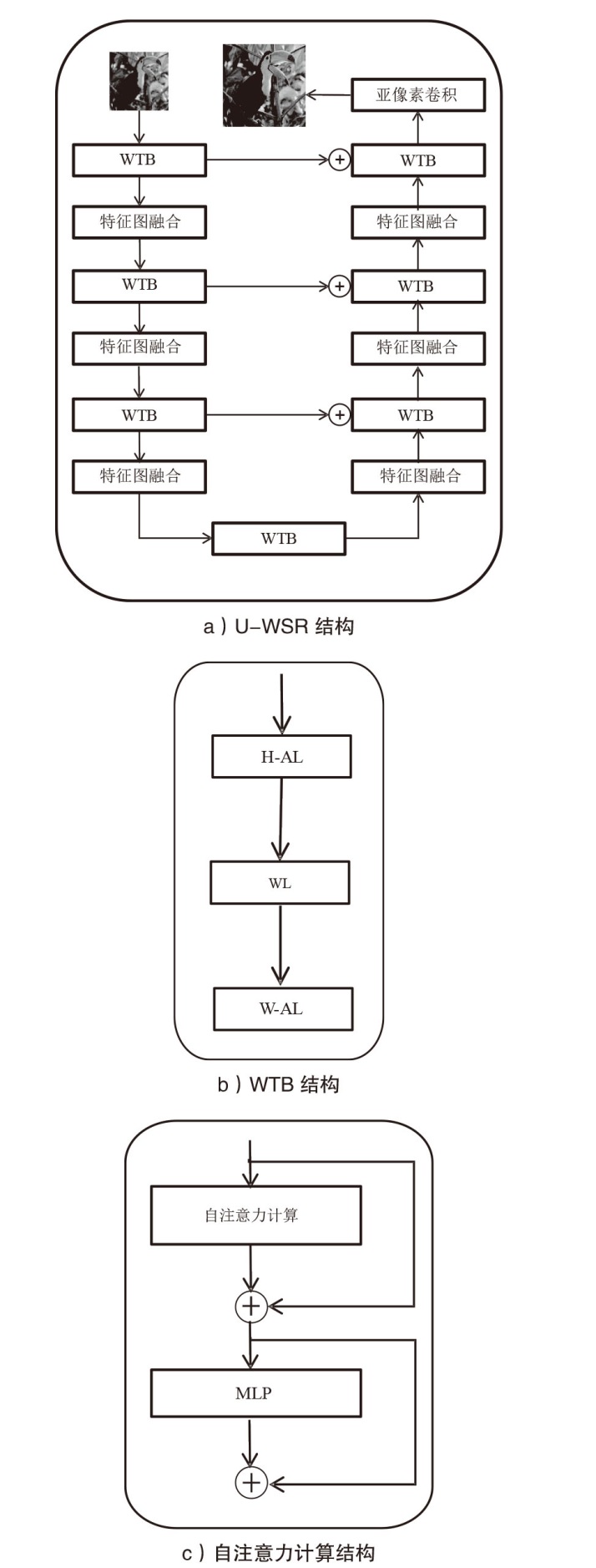
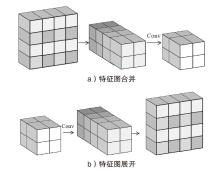
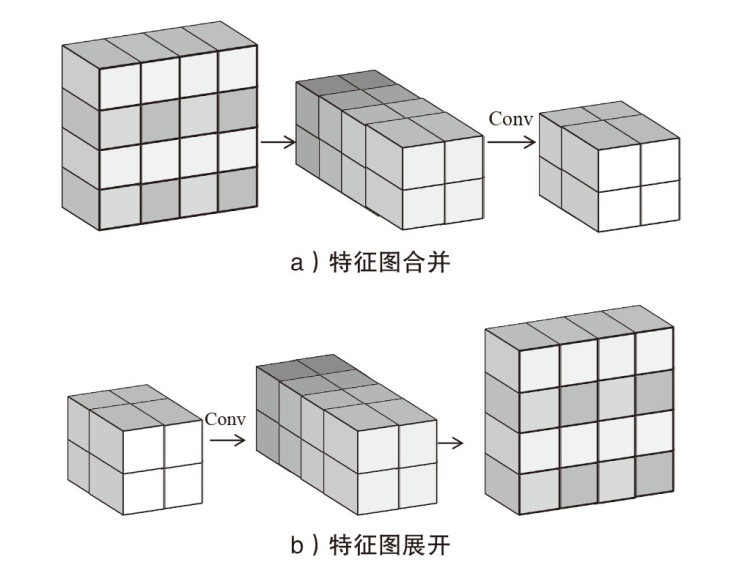
| U-WSR | |||||||||||||
| Inc-v3 | 99.3% | 94.3% | 85.3% | 98.1% | 97.3% | 96.3% | 97.1% | 96.6% | 96.9% | 97.3% | 96.6% | 74.5% | 36.5% |
| Res-50 | 95.6% | 90.1% | 70.3% | 95.6% | 95.4% | 93.6% | 94.3% | 94.5% | 94.3% | 93.5% | 92.6% | 66.8% | 37.9% |
| IncRes-v2 | 98.9% | 96.5% | 92.3% | 96.9% | 96.7% | 96.8% | 96.9% | 97.6% | 95.5% | 97.0% | 95.8% | 75.3% | 42.3% |
| 数据集 | 网络模型 | 无防御 方法 | JPEG 压缩 | R&P | TVM+ Image Quilting | Pixel Deflection | SR-ResNet | 小波去噪+EDSR | U-WSR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ILSVRC | Inc-v3 | 100.0% | 96.0% | 97.3% | 96.2% | 91.9% | 94.0% | 97.0% | 99.3% |
| Res-50 | 100.0% | 92.8% | 92.5% | 93.1% | 92.7% | 92.8% | 93.9% | 95.6% | |
| IncRes-v2 | 100.0% | 95.5% | 98.7% | 95.6% | 92.1% | 95.2% | 98.2% | 98.9% | |
| NIPS-DEV | Inc-v3 | 95.9% | 89.7% | 92.0% | 88.8% | 86.5% | 88.3% | 90.9% | 92.6% |
| Res-50 | 98.9% | 86.9% | 90.6% | 85.6% | 87.8% | 86.8% | 86.9% | 96.9% | |
| IncRes-v2 | 99.4% | 94.5% | 98.9% | 87.9% | 88.9% | 90.3% | 92.9% | 99.5% |
| 攻击方法 优化方法 | 没有防御 | SR-ResNet | EDSR | U-WSR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 良性样本 | 100.0% | 94.0% | 96.2% | 99.3% |
| FGSM-2 | 31.7% | 89.5% | 92.6% | 95.3% |
| FGSM-10 | 30.5% | 69.9% | 73.3% | 76.4% |
| I-FGSM | 11.4% | 93.4% | 95.9% | 97.3% |
| MI-FGSM | 1.7% | 92.6% | 95.2% | 97.6% |
| PGD | 1.1% | 91.5% | 93.4% | 95.4% |
| L-BFGS | 0.3% | 92.1% | 94.4% | 96.8% |
| C&W | 0.8% | 93.3% | 95.6% | 98.1% |
| JSMA | 0.8% | 90.4% | 93.6% | 95.1% |
| DeepFool | 0.4% | 93.2% | 95.5% | 97.6% |
| ZOO | 1.0% | 90.8% | 93.5% | 95.8% |
| DI2FGSM | 1.4% | 54.3% | 57.2% | 60.8% |
| MDI2FGSM | 0.6% | 24.9% | 27.1% | 30.6% |
| 攻击方法 优化方法 | 没有防御 | SR-ResNet | EDSR | U-WSR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 良性样本 | 100% | 92.8% | 93.9% | 95.6% |
| FGSM-2 | 12.2% | 85.5% | 86.1% | 90.1% |
| FGSM-10 | 6.1% | 62.3% | 64.9% | 70.3% |
| I-FGSM | 3.4% | 90.8% | 92.3% | 95.6% |
| MI-FGSM | 0.4% | 90.6% | 92.0% | 95.4% |
| PGD | 0.2% | 91.1% | 92.3% | 93.6% |
| L-BFGS | 0.1% | 90.8% | 92.6% | 94.3% |
| C&W | 0.1% | 92.1% | 93.1% | 94.5% |
| JSMA | 0.2% | 89.9% | 92.1% | 94.3% |
| DeepFool | 1.0% | 90.5% | 91.5% | 93.5% |
| ZOO | 0.8% | 89.8% | 90.1% | 92.6% |
| DI2FGSM | 0.3% | 60.1% | 60.7% | 66.8% |
| MDI2FGSM | 0.2% | 29.8% | 31.9% | 37.9% |
| 攻击方法 优化方法 | 没有防御 | SR-ResNet | EDSR | U-WSR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 良性样本 | 100% | 95.2% | 98.2% | 98.9% |
| FGSM-2 | 59.4% | 92.6% | 95.3% | 96.5% |
| FGSM-10 | 53.6% | 79.9% | 82.3% | 92.3% |
| I-FGSM | 21.6% | 94.2% | 95.8% | 96.9% |
| MI-FGSM | 0.5% | 93.1% | 95.0% | 96.7% |
| PGD | 0.3% | 92.9% | 94.3% | 96.8% |
| L-BFGS | 0.1% | 93.5% | 95.6% | 96.9% |
| C&W | 0.3% | 94.2% | 95.6% | 97.6% |
| JSMA | 0.1% | 92.3% | 94.8% | 95.5% |
| DeepFool | 0.1% | 94.1% | 96.0% | 97.0% |
| ZOO | 0.8% | 94.3% | 95.7% | 95.8% |
| DI2FGSM | 1.5% | 65.2% | 69.8% | 75.3% |
| MDI2FGSM | 0.6% | 36.6% | 35.6% | 42.3% |
| [1] | SZEGEDY C, ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I, et al. Intriguing Properties of Neural Networks[C]// ICLR.The 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations. Banff: ICLR, 2014: 1-10. |
| [2] | TABELINI L, BERRIEL R, PAIXAO T M, et al. Polylanenet: Lane Estimation via Deep Polynomial Regression[C]// IEEE. 2020 the 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). New York: IEEE, 2021: 6150-6156. |
| [3] | SUN Yifan, XU Qin, LI Yali, et al. Perceive Where to Focus: Learning Visibility-Aware Part-Level Features for Partial Person Re-Identification[C]// IEEE. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2019: 393-402. |
| [4] | LIU Dongchuan, NOCEDAL J. On the Limited Memory BFGS Method for Large Scale Optimization[J]. Mathematical Programming, 1989, 45(1): 503-528. |
| [5] | CARLINI N, WAGNER D. Towards Evaluating the Robustness of Neural Networks[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. New York: IEEE, 2017: 39-57. |
| [6] | GOODFELLOW I J, SHLENS J, SZEGEDY C. Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples[EB/OL]. (2015-03-20)[2024-09-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6572. |
| [7] | KURAKIN A, GOODFELLOW I, BENGIO S. Adversarial Examples in the Physical World[EB/OL]. (2016-07-08)[2024-09-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.02533. |
| [8] | MADRY A, MAKELOV A, SCHMIDT L, et al. Towards Deep Learning Models Resistant to Adversarial Attacks[EB/OL]. (2017-07-20)[2024-09-12]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1706.06083. |
| [9] | DONG Yinpeng, LIAO Fangzhou, PANG Tianyu, et al. Boosting Adversarial Attacks with Momentum[C]// IEEE. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2018: 9185-9193. |
| [10] | MOOSAVI-DEZFOOLI S M, FAWZI A, FROSSARD P. Deepfool: A Simple and Accurate Method to Fool Deep Neural Networks[C]// IEEE.Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2016: 2574-2582. |
| [11] | MOOSAVI-DEZFOOLI S M, FAWZI A, FAWZI O, et al. Universal Adversarial Perturbations[C]// IEEE. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2017: 1765-1773. |
| [12] | BALUJA S, FISCHER I. Learning to Attack: Adversarial Transformation Networks[EB/OL]. (2018-04-29)[2024-09-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.09387. |
| [13] | HAYES J, DANEZIS G. Learning Universal Adversarial Perturbations with Generative Models[C]// IEEE.IEEE Security and Privacy Workshops (SPW). New York: IEEE, 2018: 43-49. |
| [14] | DZIUGAITE G K, GHAHRAMANI Z, ROY D M. A Study of the Effect of JPG Compression on Adversarial Images[EB/OL]. (2016-08-02)[2024-09-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.00853. |
| [15] | LIAO Fangzhou, LIANG Ming, DONG Yinpeng, et al. Defense Against Adversarial Attacks Using High-Level Representation Guided Denoiser[C]// IEEE. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2018: 1778-1787. |
| [16] | JIA Xiaojun, WEI Xingxing, CAO Xiaochun, et al. Comdefend: An Efficient Image Compression Model to Defend Adversarial Examples[C]// IEEE. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2019: 6084-6092. |
| [17] | MUSTAFA A, KHAN S H, HAYAT M, et al. Image Super-Resolution as a Defense Against Adversarial Attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 29: 1711-1724. |
| [18] | LIM B, SON S, KIM H, et al. Enhanced Deep Residual Networks for Single Image Super-Resolution[C]// IEEE. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. New York: IEEE, 2017: 136-144. |
| [19] | VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is All You Need[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017, 30: 5998-6009. |
| [20] | DONG Xiaoyi, BAO Jianmin, CHEN Dongdong, et al. CSWin Transformer: A General Vision Transformer Backbone with Cross-Shaped Windows[C]// IEEE. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2022: 12124-12134. |
| [21] | SHI Wenzhe, CABALLERO J, HUSZAR F, et al. Real-Time Single Image and Video Super-Resolution Using an Efficient Sub-Pixel Convolutional Neural Network[C]// IEEE.Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2016: 1874-1883. |
| [22] | DENG Jia, DONG Wei, SOCHER R, et al. Imagenet: A Large-Scale Hierarchical Image Database[C]// IEEE. 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2009: 248-255. |
| [23] | KURAKIN A, GOODFELLOW I, BENGIO S, et al. Adversarial Machine Learning at Scale[EB/OL]. (2016-11-04)[2024-09-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.01236. |
| [24] | PAPERNOT N, MCDANIEL P, JHA S, et al. The Limitations of Deep Learning in Adversarial Settings[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS&P). New York: IEEE, 2016: 372-387. |
| [25] | CHEN Pinyu, ZHANG Huan, SHARMA Y, et al. Zoo: Zeroth Order Optimization Based Black-Box Attacks to Deep Neural Networks without Training Substitute Models[C]// ACM. The 10th ACM Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security. New York: ACM, 2017: 15-26. |
| [26] | XIE Cihang, ZHANG Zhishuai, ZHOU Yuyin, et al. Improving Transferability of Adversarial Examples with Input Diversity[C]// IEEE. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2019: 2730-2739. |
| [27] | DAS N, SHANBHOGUE M, CHEN S T, et al. Shield: Fast, Practical Defense and Vaccination for Deep Learning Using JPEG Compression[C]// ACM. The 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2018: 196-204. |
| [28] | XIE Cihang, WANG Jianyu, ZHANG Zhishuai, et al. Mitigating Adversarial Effects through Randomization[EB/OL]. (2017-09-08)[2024-09-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.01991. |
| [29] | GUO Chuan, RANA M, CISSE M, et al. Countering Adversarial Images Using Input Transformations[EB/OL]. (2017-06-18)[2024-09-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.00117. |
| [30] | PRAKASH A, MORAN N, GARBER S, et al. Deflecting Adversarial Attacks with Pixel Deflection[C]// IEEE. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2018: 8571-8580. |
| [31] | LEDIG C, THEIS L, HUSZAR F, et al. Photo-Realistic Single Image Super-Resolution Using a Generative Adversarial Network[C]// IEEE. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2017: 4681-4690. |
| [1] | CHEN Yonghao, CAI Manchun, ZHANG Yiwen, PENG Shufan, YAO Lifeng, ZHU Yi. A Multi-Scale and Multi-Level Feature Fusion Approach for Deepfake Face Detection [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(9): 1456-1464. |
| [2] | WANG Xinmeng, CHEN Junbao, YANG Yitao, LI Wenjin, GU Dujuan. Bayesian Optimized DAE-MLP Malicious Traffic Identification Model [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(9): 1465-1472. |
| [3] | JIN Zhigang, LI Zimeng, CHEN Xuyang, LIU Zepei. Review of Network Intrusion Detection System for Unbalanced Data [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(8): 1240-1253. |
| [4] | WANG Gang, GAO Yunpeng, YANG Songru, SUN Litao, LIU Naiwei. A Survey on Deep Learning-Based Encrypted Malicious Traffic Detection Methods [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(8): 1276-1301. |
| [5] | ZHANG Xinglan, TAO Kejin. Universal Perturbations Generation Method Based on High-Level Features and Important Channels [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(5): 767-777. |
| [6] | JIN Zengwang, JIANG Lingyang, DING Junyi, ZHANG Huixiang, ZHAO Bo, FANG Pengfei. A Review of Research on Industrial Control System Security [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(3): 341-363. |
| [7] | CHEN Hongsong, LIU Xinrui, TAO Zimei, WANG Zhiheng. A Survey of Anomaly Detection Model for Time Series Data Based on Deep Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(3): 364-391. |
| [8] | LI Hailong, CUI Zhian, SHEN Xieyang. Overview of Anomaly Analysis and Detection Methods for Network Traffic [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 194-214. |
| [9] | WU Haoying, CHEN Jie, LIU Jun. Improved Neural Network Differential Distinguisher of Simon32/64 and Simeck32/64 [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 249-259. |
| [10] | JIN Di, REN Hao, TANG Rui, CHEN Xingshu, WANG Haizhou. Research on Offensive Language Detection in Social Networks Based on Emotion-Assisted Multi-Task Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 281-294. |
| [11] | CHEN Xiaojing, TAO Yang, WU Baiqi, DIAO Yunfeng. Optimization Gradient Perception Adversarial Attack for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(9): 1386-1395. |
| [12] | XU Ruzhi, ZHANG Ning, LI Min, LI Zixuan. Research on a High Robust Detection Model for Malicious Software [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(8): 1184-1195. |
| [13] | TIAN Zhao, NIU Yajie, SHE Wei, LIU Wei. A Reputation Evaluation Method for Vehicle Nodes in V2X [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(5): 719-731. |
| [14] | ZHANG Guanghua, LIU Yichun, WANG He, HU Boning. Defense Scheme for Removing Deep Neural Network Backdoors Based on JSMA Adversarial Attacks [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(4): 545-554. |
| [15] | XU Zirong, GUO Yanping, YAN Qiao. Malicious Software Adversarial Defense Model Based on Feature Severity Ranking [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(4): 640-649. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||