Netinfo Security ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (8): 1276-1301.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.08.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
A Survey on Deep Learning-Based Encrypted Malicious Traffic Detection Methods
WANG Gang1( ), GAO Yunpeng1, YANG Songru2, SUN Litao3, LIU Naiwei1
), GAO Yunpeng1, YANG Songru2, SUN Litao3, LIU Naiwei1
- 1. School of Data Science and Application, Inner Mongolia University of Technology, Hohhot 010080, China
2. Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Public Security Bureau, Hohhot 010050, China
3. Education Examinations Authority of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Hohhot 010010, China
-
Received:2025-04-16Online:2025-08-10Published:2025-09-09
CLC Number:
Cite this article
WANG Gang, GAO Yunpeng, YANG Songru, SUN Litao, LIU Naiwei. A Survey on Deep Learning-Based Encrypted Malicious Traffic Detection Methods[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(8): 1276-1301.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://netinfo-security.org/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.08.009
| 文献 | 年份 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 文献[ | 2020 | 采用“六步法”的一般检测框架模型对检测过程进行详细论述,并整理了主流公开数据集 |
| 文献[ | 2021 | 对网络流量的侧信道攻击原理进行总结归纳,并从攻、防两个角度对网络流量的侧信道攻击的研究进展进行详细阐述 |
| 文献[ | 2022 | 对TLS协议恶意加密流量识别工作进行综述,包括基于机器学习和基于深度学习的研究成果,以及现有工作的不足,并对未来工作和发展趋势进行展望 |
| 文献[ | 2021 | 通过系统性框架和实验分析,为加密恶意流量检测提供了方法论与数据基础 |
| 文献[ | 2023 | 对现有检测、分类和识别方法,从多个粒度和角度进行划分,系统性地归纳与比较现有研究的优缺点 |
| 文献[ | 2022 | 按分析目标而非技术类型组织文献,提出了一个通用的工作流程框架,并详细讨论了不同分析目标下的研究 |
| 文献[ | 2024 | 系统综述探讨了深度学习在加密数据上进行隐私保护入侵检测的进展 |
| 数据集 | 年份 | 描述 | 加密 | 平衡 | 优缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDN-SlowRate-DDoS[ | 2023 | 使用SN4I的物理设备部署了基于SDN的数据中心拓扑,其中包含两个主干交换机和4个枝叶交换机 | 是 | 是 | 优点:针对IoT设备和5G等下一代网络的新 威胁 缺点:攻击行为单一 |
| CIC-MalMem-2022[ | 2022 | 该数据集由50%的恶意软件和50%的良性软件组成,总共包含58596条记录 | 是 | 是 | 优点:正常流量与恶意流量平衡 缺点:不完全加密流量 |
| CIRA-CIC-DoHBrw-2020[ | 2020 | 使用5个不同的浏览器/工具和4台服务器在应用程序中实现DoH协议,以捕获Benign-DoH、Malicious-DoH和non-DoH流量 | 是 | 否 | 优点:加密流量 缺点:仅针对DNS协议 |
| CIC-MalDroid-2020[ | 2020 | 从多个来源收集超过17341个Android样本,包括VirusTotal服务、Contagio、AMD、MalDozer和最近研究中使用的其他数据集 | 是 | 是 | 优点:包括完整捕获的静态和 动态特征 缺点:采集范围受限 |
| IoT-23[ | 2020 | IoT-23是来自IoT设备网络流量的新数据集,在IoT设备中执行了20个恶意软件捕获,以及3个针对良性IoT设备流量的捕获 | 部分 | 是 | 优点:采集真实IoT设备流量 缺点:大部分流量未加密 |
| BoT-IoT[ | 2019 | BoT-IoT是通过在新南威尔士大学堪培拉网络中心的网络靶场实验室设计一个真实的网络环境而创建的 | 是 | 否 | 优点:数据量大 缺点:数据不平衡 |
| CIC-IDS-2017[ | 2017 | 该数据集基于HTTP、HTTPS、FTP、SSH和电子邮件协议的25个用户的抽象行为,通过B-Profile系统产生自然背景良性流量 | 是 | 否 | 优点:数据集符合10项标准 缺点:正常用户行为由脚本产生 |
| CIC-AndMal2017[ | 2017 | 采集自真实的智能手机上运行的恶意软件和良性应用程序,共计4354个恶意软件和6500个良性样本 | 是 | 是 | 优点:包含隐蔽性攻击 缺点:数据量 较小 |
| NDSec-1[ | 2016 | 数据集包括有效载荷在内的原始网络跟踪以及系统日志和窗口事件日志,并使用YAF捕获的双向流 | 是 | 是 | 优点:包含多类型攻击数据 缺点:没有正常流量 |
| ISCX VPN-nonVPN[ | 2016 | 数据集捕获了一个常规会话和一个通过VPN的会话,共有14个流量类别 | 部分 | 否 | 优点:良性流量具有多样性 缺点:缺乏攻击流量 |
| UNSW-NB15[ | 2015 | 数据集由澳大利亚网络安全中心的网络靶场实验室创建,包含82332条记录的训练集,175341条记录的测试集 | 是 | 否 | 优点:数据 规模大 缺点:不是真实流量 |
| CTU-13[ | 2013 | 该数据集的目标是大量捕获真实僵尸网络流量,包含不同僵尸网络样本的13个捕获场景 | 部分 | 否 | 优点:包含13种僵尸网络场景 缺点:数据 不平衡 |
| NSL-KDD[ | 2009 | NSL-KDD数据集是KDD99数据集的修订版本,数据集的每条记录包含43个特征,其中,41个特征指的是流量输入本身,最后两个特征是标签(正常或攻击)和分数 | 否 | 否 | 优点:数据集相对平衡 缺点:不针对 加密流量 |
| 解决层面 | 文献 | 策略 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数据层面 | 文献[ | Cluster-SMOTE | 容易实现,效率较高 | 存在边界模糊风险和信息丢失风险,生成质量不如GAN等生成模型 |
| 文献[ | MSH-GAN | 能够挖掘流量的深层次特征,生成数据具有真实性 | 易陷入局部最优 | |
| 文献[ | VAE | 能够准确地重建数据并更好地保留原始 分布 | 存在模式崩溃问题 | |
| 文献[ | 扩散模型 | 减轻模式崩溃问题,训练过程更稳定 | 计算成本高,训练和推理速度慢 | |
| 算法层面 | 文献[ | CAB | 自适应调整类别权重,不需要引入额外的 数据 | 可能影响多数类的 性能 |
| 文献[ | 可变最小置信度阈值 | 相较于CAB,可变最小置信度阈值可以兼顾准确率和召回率,减少错误分类 | 阈值优化会受数据质量影响 | |
| 文献[ | 自适应平衡训练方法 | 可以根据数据的实际分布自动调整策略,而不是依赖于人为设定的类别比例或权重 | 在极端不平衡的情况下,效果比较差 | |
| 文献[ | 引力计算 | 能以数据增强方法相结合,共同优化数据不平衡问题 | 引力计算会受到维度灾难影响,导致计算效率下降 |
| 特征 类型 | 核心优势 | 技术局限 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 统计 特征 | 单流处理延迟低;专家规则可解释性强;特征维度低 | 信息损失大;新型APT攻击漏报率高 | 资源受限的边缘设备实时检测;工业控制网络异常告警;运营商级DDoS快速筛查 |
| 时序 特征 | 行为建模强;支持跨协议行为分析;可检测低频隐蔽信道 | 存在时序失真;内存消耗大 | APT攻击中的低频隐蔽通信检测;暗网流量行为分析;物联网设备周期性通信监测 |
| 原始流特征 | 支持恶意软件家族细粒度分类;深度特征挖掘;端到端学习避免人工特征偏差 | 计算成本高;隐私合规风险 | 协议指纹精细识别;恶意载荷深度取证分析 |
| 频域 特征 | 抗时序噪声干扰;特征维度低 | 难以还原完整时序行为;需要人工干预 | 工业时序攻击(如PLC脉冲注入);频分复用隐蔽信道检测 |
| 类别 | 适用场景 | 文献 | 方法 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 过滤法 | 高维数据预处理 | 文献[ | 最大信息系数、皮尔逊 系数 | 灵活性强、计算效率高 | 对异常值敏感、较难解释 |
| 文献[ | 卡方检验、 熵阈值 | 适合离散数据、高效 | 对频数要求较高、阈值设定难 | ||
| 文献[ | 信息论、 图模型 | 有较强理论基础、能够捕捉到线性和非线性关系 | 计算复杂度高、对噪声敏感 | ||
| 包装法 | 小规模数据,需高精度 | 文献[ | 递归特征消除 | 适应性强、具有一定 可解释性 | 对模型的依赖性强(该文依赖信息增益的计算) |
| 文献[ | 遗传算法 | 进行了可解释性分析 | 收敛速度慢 | ||
| 嵌入法 | 大规模数据,端到端训练 | 文献[ | L1正则化 | 自动特征选择、效率得到了提升 | 正则化系数过高,容易导致过拟合 |
| 文献[ | SHAP | 能够为每个特征提供一个直观的贡献值,并且可以提供可解释性 | 在特征数较多时,会导致计算复杂度较高 | ||
| 文献[ | XGBoost | 高效处理高维数据,支持并行计算,适合类别不平衡 问题 | 需要进行数据预处理,对异常值较敏感 |
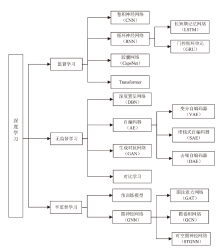
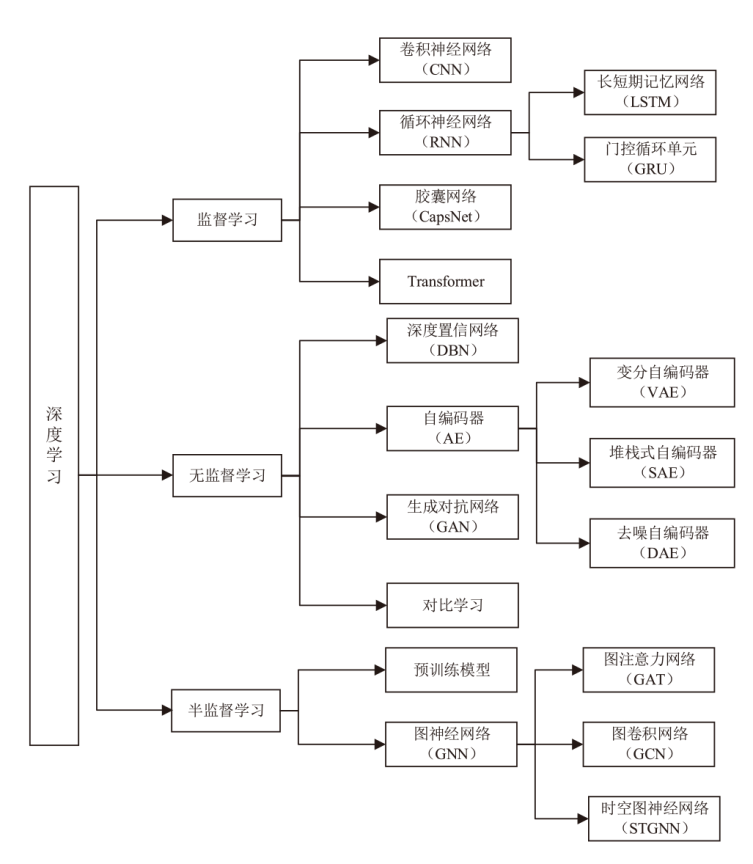
| 学习 范式 | 文献 | 分类模型 | 数据集 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
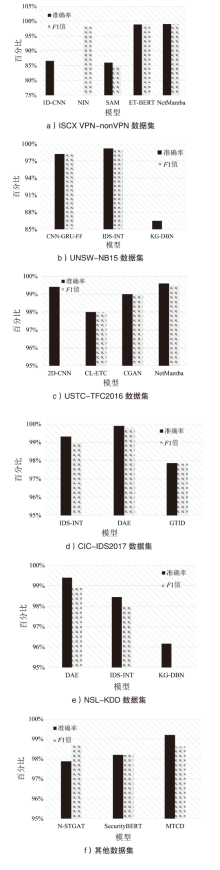
| 监督 学习 | 文献[ | 1D-CNN | ISCX VPN-nonVPN | 能够高效处理序列数据 | 长序列建模能力有限 |
| 文献[ | NIN | ISCX VPN-nonVPN | 提高了计算 效率 | 增加了额外的通信开销 | |
| 文献[ | SAM | WIDE、 UNIBS、 ISCX VPN-nonVPN | 实时性强,支持在线流量 分类 | 无法应对数据不平衡问题 | |
| 文献[ | 2D-CNN | USTC-TFC2016 | 泛化能力强 | 易受对抗攻击 影响 | |
| 文献[ | CNN-GRU-FF | UNSW-NB15、 NSL-KDD | 能够有效处理类别不平衡 问题 | 计算资源需求高 | |
| 文献[ | IDS-INT | UNSW-NB15、 CIC-IDS2017、 NSL-KDD | 对模型的决策过程进行了 解释 | 不能满足高 吞吐场景 | |
| 文献[ | GTID | ISCX2012、 IDS2017 | 具有良好的 鲁棒性 | 未考虑未知攻击检测 | |
| 文献[ | MTCD | TCD-2022 | 具有较强的空间层级信息建模能力 | 训练不稳定,易受超参数影响 | |
| 文献[ | CapsNet | CSE-CIC-IDS2018 | 引入少量样本学习,不依赖标签数据 | 适用场景有限,在复杂流量数据上的应用还不 成熟 | |
| 无监督学习 | 文献[ | KG-DBN | NSL-KDD、 UNSW-NB15 | 能够处理处理大规模数据 | 参数选择的不确定性会影响检测准确率 |
| 文献[ | CL-ETC | USTC-TFC2016、 自建数据集 | 鲁棒性强 | 模型训练时间长 | |
| 文献[ | DAE | CICIDS2017、 NSL-KDD | 具有较强的适应能力 | 依赖数据增强 | |
| 文献[ | CGAN | ISCX2012、 USTC-TFC2016 | 解决了类别不平衡问题 | 生成时易陷入局部最优 | |
| 半监督学习 | 文献[ | ET-BERT | ISCX VPN-nonVPN、 CSTNET-TLS 1.3 | 泛化能力强且能够在少量标注数据上快速适应具体任务 | 模型解释性不足 |
| 文献[ | SecurityBERT | Edge-IIoT | 高效性,适合在资源受限的IoT设备上部署 | 对特定数据分布的适应性有限 | |
| 文献[ | MTC-MAE | USTC-TFC2016、 CIC-AndMal2017、 ISCX VPN-NonVPN | 支持多种分类场景 | 依赖预训练数据的质量 | |
| 文献[ | NetMamba | USTC-TFC2016、 ISCXVPN2016、 CICIoT2022 | 推理速度快、占用内存小 | 模型解释性不足 | |
| 文献[ | MalDiscovery | CTU-13 | 多视图特征融合高表征能力 | 计算资源需求高 | |
| 文献[ | N-STGAT | NF-BoT-IoT-v2 | 处理效率高 | 应用场景局限性 |
| [1] | WANG Liting, WANG Quan, JIN Liang, et al. Research and Application Exploration of 6G Communication Network System Architecture[C]// IEEE. 2022 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Electronic Technology, Communication and Information. New York: IEEE, 2022: 742-745. |
| [2] | DOWLING B, FISCHLIN M, GÜNTHER F, et al. A Cryptographic Analysis of the TLS 1.3 Handshake Protocol[EB/OL]. (2021-07-30)[2025-04-05]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00145-021-09384-1. |
| [3] | MARX R, HERBOTS J, LAMOTTE W, et al. Same Standards, Different Decisions:A Study of QUIC and HTTP/3 Implementation Diversity[C]// ACM. The Workshop on the Evolution, Performance, and Interoperability of QUIC. New York: ACM, 2020: 14-20. |
| [4] | BUTUN I, PEREIRA N, GIDLUND M. Analysis of LoRaWAN v1.1 Security[C]// ACM. The 4th ACM MobiHoc Workshop on Experiences with the Design and Implementation of Smart Objects. New York: ACM, 2018: 1-6. |
| [5] | JEŘÁBEK K, HYNEK K, ČEJKA T, et al. Collection of Datasets with DNS over HTTPS Traffic[EB/OL]. (2022-06-02)[2025-04-05]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352340922005121. |
| [6] | Google. HTTPS Encryption on the Web[EB/OL]. (2024-06-23)[2025-04-05]. https://transparencyreport.google.com/https/overview. |
| [7] | NING Jianting, POH G S, LOH J C, et al. PrivDPI: Privacy-Preserving Encrypted Traffic Inspection with Reusable Obfuscated Rules[C]// ACM. The 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2019: 1657-1670. |
| [8] | ZHENG Juan, ZENG Zhiyong, FENG Tao. GCN-ETA: High-Efficiency Encrypted Malicious Traffic Detection[EB/OL]. (2022-01-12)[2025-04-05]. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1155/2022/4274139. |
| [9] | WANG Yalu, LI Jie, ZHAO Wei, et al. N-STGAT: Spatio-Temporal Graph Neural Network Based Network Intrusion Detection for Near-Earth Remote Sensing[EB/OL]. (2023-07-20)[2025-04-05]. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143611. |
| [10] | LI Ziang, CHENG Zhenyu, ZANG Tianning, et al. MTCD-Model: A Two-Layer Model for Malicious Traffic Classification and Detection Based on Hierarchical Feature Learning[C]// IEEE. 2023 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. New York: IEEE, 2023: 1-8. |
| [11] | SUN Handi, WAN Liang, LIU Mengying, et al. Few-Shot Network Intrusion Detection Based on Prototypical Capsule Network with Attention Mechanism[EB/OL]. (2023-04-20)[2025-04-05]. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0284632. |
| [12] | LIN Xinjie, XIONG Gang, GOU Gaopeng, et al. ET-BERT: A Contextualized Datagram Representation with Pre-Training Transformers for Encrypted Traffic Classification[C]// ACM. The ACM Web Conference 2022. New York: ACM, 2022: 633-642. |
| [13] | HANG Zijun, LU Yuliang, WANG Yongjie, et al. Flow-Mae: Leveraging Masked Autoencoder for Accurate, Efficient and Robust Malicious Traffic Classification[C]// ACM. The 26th International Symposium on Research in Attacks, Intrusions and Defenses. New York: ACM, 2023: 297-314. |
| [14] | FERRAG M A, NDHLOVU M, TIHANYI N, et al. Revolutionizing Cyber Threat Detection with Large Language Models: A Privacy-Preserving BERT-Based Lightweight Model for IoT/IIoT Devices[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 23733-23750. |
| [15] | XU Ke, ZHANG Xixi, WANG Yu, et al. Self-Supervised Learning Malware Traffic Classification Based on Masked Autoencoder[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(10): 17330-17340. |
| [16] | WANG Tongze, XIE Xiaohui, WANG Wenduo, et al. Netmamba: Efficient Network Traffic Classification via Pre-Training Unidirectional Mamba[C]// IEEE. 2024 IEEE 32nd International Conference on Network Protocols. New York: IEEE, 2024: 1-11. |
| [17] | ZHAI Mingfang, ZHANG Xingming, ZHAO Bo. Survey of Encrypted Malicious Traffic Detection Based on Deep Learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Network and Information Security, 2020, 6(3): 66-77. |
| [18] | LI Ding, ZHU Yuefei, LU Bin, et al. Survey of Side Channel Attack on Encrypted Network Traffic[J]. Chinese Journal of Network and Information Security, 2021, 7(4): 114-130. |
| [19] |
KANG Peng, YANG Wenzhong, MA Hongqiao. TLS Malicious Encrypted Traffic Identification Research[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2022, 58(12): 1-11.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2110-0029 |
|
康鹏, 杨文忠, 马红桥. TLS 协议恶意加密流量识别研究综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2022, 58(12):1-11.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2110-0029 |
|
| [20] | WANG Zihao, FOK K W, THING V L L. Machine Learning for Encrypted Malicious Traffic Detection: Approaches, Datasets and Comparative Study[EB/OL]. (2021-11-28)[2025-04-05]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0167404821003667. |
| [21] | CHEN Zihan, CHENG Guang, XU Ziheng, et al. A Survey on Internet Encrypted Traffic Detection, Classification, and Identification[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2023, 46(5): 1060-1085. |
| 陈子涵, 程光, 徐子恒, 等. 互联网加密流量检测、分类与识别研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2023, 46(5):1060-1085. | |
| [22] | SHEN Meng, YE Ke, LIU Xingtong, et al. Machine Learning-Powered Encrypted Network Traffic Analysis: A Comprehensive Survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2022, 25(1): 791-824. |
| [23] | HENDAOUI F, FERCHICHI A, TRABELSI L, et al. Advances in Deep Learning Intrusion Detection over Encrypted Data with Privacy Preservation: A Systematic Review[J]. Cluster Computing, 2024, 27(7): 8683-8724. |
| [24] | FELT A P, BARNES R, KING A, et al. Measuring HTTPS Adoption on the Web[C]// USENIX. The 26th USENIX Security Symposium. Berkeley: USENIX, 2017: 1323-1338. |
| [25] | WANG Zhenhui, HAN Dezhi, LI Ming, et al. The Abnormal Traffic Detection Scheme Based on PCA and SSH[J]. Connection Science, 2022, 34(1): 1201-1220. |
| [26] | LÓPEZ-MILLÁN G, MARÍN-LÓPEZ R, PEREÑÍGUEZ-GARCÍA F, et al. Analysis and Practical Validation of a Standard SDN-Based Framework for IPsec Management[EB/OL]. (2022-07-20)[2025-04-05]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0920548922000393. |
| [27] | LANGLEY A, RIDDOCH A, WILK A, et al. The Quic Transport Protocol: Design and Internet-Scale Deployment[C]// ACM. The Conference of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication. New York: ACM, 2017: 183-196. |
| [28] | CREMERS C, HORVAT M, HOYLAND J, et al. A Comprehensive Symbolic Analysis of TLS 1.3[C]// ACM. The 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2017: 1773-1788. |
| [29] | MÖLLER B, DUONG T, KOTOWICZ K. This POODLE Bites: Exploiting the SSL 3.0 Fallback[J]. Security Advisory, 2014, 21: 34-58. |
| [30] | YUNGAICELA-NAULA N M, VARGAS-ROSALES C, PEREZ-DIAZ J A, et al. Physical Assessment of an SDN-Based Security Framework for DDoS Attack Mitigation: Introducing the SDN-SlowRate-DDoS Dataset[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 46820-46831. |
| [31] | CARRIER T, VICTOR P, TEKEOGLU A, et al. Detecting Obfuscated Malware Using Memory Feature Engineering[C]// Springer. The 8th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy. Heidelberg: Springer, 2021: 177-188. |
| [32] | MONTAZERISHATOORI M, DAVIDSON L, KAUR G, et al. Detection of Doh Tunnels Using Time-Series Classification of Encrypted Traffic[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE Intl Conf on Dependable, Autonomic and Secure Computing, Intl Conf on Pervasive Intelligence and Computing, Intl Conf on Cloud and Big Data Computing, Intl Conf on Cyber Science and Technology Congress. New York: IEEE, 2020: 63-70. |
| [33] | MAHDAVIFAR S, KADIR A F A, FATEMI R, et al. Dynamic Android Malware Category Classification Using Semi-Supervised Deep Learning[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE Intl Conf on Dependable, Autonomic and Secure Computing, Intl Conf on Pervasive Intelligence and Computing, Intl Conf on Cloud and Big Data Computing, Intl Conf on Cyber Science and Technology Congress. New York: IEEE, 2020: 515-522. |
| [34] | GARCIA S, PARMISANO A, ERQUIAGA M J. IoT-23:A Labeled Dataset with Malicious and Benign IoT Network Traffic[EB/OL]. [2025-04-05]. https://www.stratosphereips.org/datasets-iot23. |
| [35] | KORONIOTIS N, MOUSTAFA N, SITNIKOVA E, et al. Towards the Development of Realistic Botnet Dataset in the Internet of Things for Network Forensic Analytics: Bot-Iot Dataset[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2019, 100: 779-796. |
| [36] | SHARAFALDIN I, LASHKARI A H, GHORBANI A A. Toward Generating a New Intrusion Detection Dataset and Intrusion Traffic Characterization[J]. ICISSP, 2018, 1(2018): 108-116. |
| [37] | LASHKARI A H, KADIR A F A, TAHERI L, et al. Toward Developing a Systematic Approach to Generate Benchmark Android Malware Datasets and Classification[C]// IEEE. 2018 International Carnahan Conference on Security Technology. New York: IEEE, 2018: 1-7. |
| [38] | BEER F, HOFER T, KARIMI D, et al. A New Attack Composition for Network Security[C]// DFN-Verein. DFN-Forum Kommunikation stechnologien. Bonn: Gesellschaft Für Informatik EV, 2017: 11-20. |
| [39] | DRAPER-GIL G, LASHKARI A H, MAMUN M S I, et al. Characterization of Encrypted and Vpn Traffic Using Time-Related[C]// Springer. The 2nd International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy. Heidelberg: Springer, 2016: 407-414. |
| [40] | MOUSTAFA N, SLAY J.UNSW-NB15:A Comprehensive Data Set for Network Intrusion Detection Systems (UNSW-NB15 Network Data Set)[C]// IEEE. 2015 Military Communications and Information Systems Conference. New York: IEEE, 2015: 1-6. |
| [41] | GARCIA S, GRILL M, STIBOREK J, et al. An Empirical Comparison of Botnet Detection Methods[J]. Computers & Security, 2014, 45: 100-123. |
| [42] | TAVALLAEE M, BAGHERI E, LU Wei, et al. A Detailed Analysis of the KDD CUP 99 Data Set[C]// IEEE. 2009 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence for Security and Defense Applications. New York: IEEE, 2009: 1-6. |
| [43] | GOYAL P, GOYAL A. Comparative Study of Two Most Popular Packet Sniffing Tools-Tcpdump and Wireshark[C]// IEEE. 2017 9th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks. New York: IEEE, 2017: 77-81. |
| [44] | BANERJEE U, VASHISHTHA A, SAXENA M. Evaluation of the Capabilities of WireShark as a Tool for Intrusion Detection[J]. International Journal of Computer Applications, 2010, 6(7): 1-5. |
| [45] | TIWARI A, SARASWAT S, DIXIT U, et al. Refinements in Zeek Intrusion Detection System[C]// IEEE. 2022 8th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems. New York: IEEE, 2022: 974-979. |
| [46] | GONEN S, KARACAYILMAZ G, ARTUNER H, et al. Cyber Attack Detection with Encrypted Network Connection Analysis[C]// Springer. International Symposium on Intelligent Manufacturing and Service Systems. Heidelberg: Springer, 2023: 622-629. |
| [47] | HOFSTEDE R, ČELEDA P, TRAMMELL B, et al. Flow Monitoring Explained: From Packet Capture to Data Analysis with Netflow and Ipfix[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2014, 16(4): 2037-2064. |
| [48] | BAYDOĞMUŞ G K. The Effects of Normalization and Standardization an Internet of Things Attack Detection[J]. Avrupa Bilim ve Teknoloji Dergisi, 2021(29): 187-192. |
| [49] | HONG Danghong, NGUYEN H D. A PCA-Based Method for IoT Network Traffic Anomaly Detection[C]// IEEE. 2018 20th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology. New York: IEEE, 2018: 381-386. |
| [50] | SONG Jiaming, WANG Xiaojuan, HE Mingshu, et al. CSK-CNN: Network Intrusion Detection Model Based on Two-Layer Convolution Neural Network for Handling Imbalanced Dataset[EB/OL]. (2023-02-13)[2025-04-05]. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14020130. |
| [51] | PARK S, PARK H. Combined Oversampling and Undersampling Method Based on Slow-Start Algorithm for Imbalanced Network Traffic[J]. Computing, 2021, 103(3): 401-424. |
| [52] | HUI Shuodi, WANG Huandong, WANG Zhenhua, et al. Knowledge Enhanced GAN for IoT Traffic Generation[C]// ACM. The ACM Web Conference 2022. New York: ACM, 2022: 3336-3346. |
| [53] | LI Tong, HUI Shiyuan, ZHANG Shiyuan, et al. Mobile User Traffic Generation via Multi-Scale Hierarchical GAN[J]. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data, 2024, 18(8): 1-19. |
| [54] | WANG Pan, LI Shuhang, YE Feng, et al. PacketCGAN: Exploratory Study of Class Imbalance for Encrypted Traffic Classification Using CGAN[C]// IEEE. ICC 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC). New York: IEEE, 2020: 1-7. |
| [55] | WANG Haizhen, YAN Jinying, JIA Na. A New Encrypted Traffic Identification Model Based on VAE-LSTM-DRN[J]. Computers, Materials & Continua, 2024, 78(1): 569-588. |
| [56] | NOBLET G, LEFEBVRE C, OWEZARSKI P, et al. NetGlyph: Representation Learning to Generate Network Traffic with Transformers[C]// IEEE. 2024 20th International Conference on Network and Service Management. New York: IEEE, 2024: 1-9. |
| [57] | SIVAROOPAN N, BANDARA D, MADARASINGHA C, et al. Netdiffus: Network Traffic Generation by Diffusion Models through Time-Series Imaging[EB/OL]. (2024-07-10)[2025-04-05]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1389128624004481. |
| [58] | REDDY P C S, MULLER P S, KOKA S N, et al. Detection of Encrypted and Malicious Network Traffic Using Deep Learning[C]// IEEE. 2023 International Conference on Ambient Intelligence, Knowledge Informatics and Industrial Electronics. New York: IEEE, 2023: 1-6. |
| [59] | LIU Weike, ZHU Cheng, DING Zhaoyun, et al. Multiclass Imbalanced and Concept Drift Network Traffic Classification Framework Based on Online Active Learning[EB/OL]. (2022-11-24)[2025-04-05]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0952197622005978. |
| [60] | LIN Kunda, XU Xiaolong, XIAO Fu. MFFusion: A Multi-Level Features Fusion Model for Malicious Traffic Detection Based on Deep Learning[EB/OL]. (2021-12-08)[2025-04-05]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1389128621005399. |
| [61] | CHEN Zhenxiang, YAN Qiben, HAN Hongbo, et al. Machine Learning Based Mobile Malware Detection Using Highly Imbalanced Network Traffic[J]. Information Sciences, 2018, 433: 346-364. |
| [62] | SARKAR D, VINOD P, YERIMA S Y. Detection of Tor Traffic Using Deep Learning[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE/ACS 17th International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications. New York: IEEE, 2020: 1-8. |
| [63] | HE Huijie, LAI Yingxu, WANG Yipeng, et al. A Data Skew-Based Unknown Traffic Classification Approach for TLS Applications[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2023, 138: 1-12. |
| [64] | BURNAP P, FRENCH R, TURNER F, et al. Malware Classification Using Self Organising Feature Maps and Machine Activity Data[J]. Computers & Security, 2018, 73: 399-410. |
| [65] | ZHANG Xueqin, ZHAO Min, WANG Jiyuan, et al. Deep-Forest-Based Encrypted Malicious Traffic Detection[EB/OL]. (2022-03-22)[2025-04-05]. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11070977. |
| [66] | KOUMAR J, HYNEK K, ČEJKA T. Network Traffic Classification Based on Single Flow Time Series Analysis[C]// IEEE. 2023 19th International Conference on Network and Service Management. New York: IEEE, 2023: 1-7. |
| [67] | WANG Wei, ZHU Ming, ZENG Xuewen, et al. Malware Traffic Classification Using Convolutional Neural Network for Representation Learning[C]// IEEE. 2017 International Conference on Information Networking. New York: IEEE, 2017: 712-717. |
| [68] | MAKRI E, AGRAFIOTIS G, LALAS A, et al. A Protocol Agnostic Polymorphic Network Packet Transformer for 5G Malware Traffic Classification Using Deep Learning Models[C]// IEEE. 2024 Joint European Conference on Networks and Communications & 6G Summit. New York: IEEE, 2024: 824-829. |
| [69] | KOZIK R, PAWLICKI M, CHORAŚ M. A New Method of Hybrid Time Window Embedding with Transformer-Based Traffic Data Classification in IoT-Networked Environment[J]. Pattern Analysis and Applications, 2021, 24(4): 1441-1449. |
| [70] | HAN Xueying, CUI Susu, LIU Song, et al. Network Intrusion Detection Based on N-Gram Frequency and Time-Aware Transformer[EB/OL]. (2023-03-09)[2025-04-05]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0167404823000810. |
| [71] | HU Zhenguo, HASEGAWA H, YAMAGUCHI Y, et al. Enhancing Detection of Malicious Traffic through FPGA-Based Frequency Transformation and Machine Learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 12: 2648-2659. |
| [72] | FU Chuanpu, LI Qi, SHEN Meng, et al. Frequency Domain Feature Based Robust Malicious Traffic Detection[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2022, 31(1): 452-467. |
| [73] | NI Jiayi, CHEN Wei, TONG Jiacheng, et al. High-Speed Anomaly Traffic Detection Based on Staged Frequency Domain Features[EB/OL]. (2023-08-12)[2025-04-05]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S221421262300159X. |
| [74] |
LI Daoquan, ZHU Shengkai, ZHAI Yuyang, et al. Semi-Supervised Network Traffic Classification Based on Feature Selection and Improved Tri-Training[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2024, 60(23): 275-285.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2307-0344 |
|
李道全, 祝圣凯, 翟豫阳, 等. 基于特征选择与改进的Tri-Training的半监督网络流量分类[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2024, 60(23):275-285.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2307-0344 |
|
| [75] | NIU Weina, ZHUO Zhongliu, ZHANG Xiaosong, et al. A Heuristic Statistical Testing Based Approach for Encrypted Network Traffic Identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(4): 3843-3853. |
| [76] | TANG Hong, LIU Dan, YAO Lishuang, et al. Feature Selection Algorithm for Class Imbalanced Internet Traffic[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(4): 923-930. |
| 唐宏, 刘丹, 姚立霜, 等. 面向类不平衡网络流量的特征选择算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(4):923-930. | |
| [77] | QASEM A A, QUTQUT M H, ALHAJ F, et al. SRFE: A Stepwise Recursive Feature Elimination Approach for Network Intrusion Detection Systems[J]. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 2024, 17(6): 3634-3649. |
| [78] | GALI U M, YASMEEN M M, CHANGALA R, et al. A Dominant Feature Selection Method for Deep Learning Based Traffic Classification Using a Genetic Algorithm[J]. International Journal of Scientific Research in Computer Science, Engineering and Information Technology, 2022, 8(6): 173-181. |
| [79] | LONG Gang, ZHANG Zhaoxin. Deep Encrypted Traffic Detection: An Anomaly Detection Framework for Encryption Traffic Based on Parallel Automatic Feature Extraction[EB/OL]. (2023-03-10)[2025-04-05]. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/3316642. |
| [80] | KHANI P, MOEINADDINI E, ABNAVI N D, et al. Explainable Artificial Intelligence for Feature Selection In Network Traffic Classification: A Comparative Study[EB/OL]. (2024-04-10)[2025-04-05]. https://doi.org/10.1002/ett.4970. |
| [81] | MANJU N, HARISH B S, PRAJWAL V. Ensemble Feature Selection and Classification of Internet Traffic Using XGBoost Classifier[J]. International Journal of Computer Network and Information Security, 2019, 11(7): 37-44. |
| [82] | WANG Wei, ZHU Ming, WANG Jinlin, et al. End-to-End Encrypted Traffic Classification with One-Dimensional Convolution Neural Networks[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Intelligence and Security Informatics. New York: IEEE, 2017: 43-48. |
| [83] | BU Zhiyong, ZHOU Bin, CHENG Pengyu, et al. Encrypted Network Traffic Classification Using Deep and Parallel Network-in-Network Models[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 132950-132959. |
| [84] | XIE Guorui, LI Qing, JIANG Yong. Self-Attentive Deep Learning Method for Online Traffic Classification and Its Interpretability[EB/OL]. (2021-07-01)[2025-04-05]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1389128621002930. |
| [85] | ZHANG Yong, CHEN Xu, GUO Da, et al. PCCN: Parallel Cross Convolutional Neural Network for Abnormal Network Traffic Flows Detection in Multi-Class Imbalanced Network Traffic Flows[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 119904-119916. |
| [86] | BAZUHAIR W, LEE W. Detecting Malign Encrypted Network Traffic Using Perlin Noise and Convolutional Neural Network[C]// IEEE. 2020 10th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference. New York: IEEE, 2020: 200-206. |
| [87] | SONG Yangyang, LUKTARHAN N, SHI Zhaolei, et al. TGA: A Novel Network Intrusion Detection Method Based on TCN, BiGRU and Attention Mechanism[EB/OL]. (2023-06-27)[2025-04-05]. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12132849. |
| [88] | DU Jiawei, YANG Kai, HU Yanjing, et al. NIDS-CNNLSTM: Network Intrusion Detection Classification Model Based on Deep Learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 24808-24821. |
| [89] | IMRANA Y, XIANG Yanping, ALI L, et al. CNN-GRU-FF: A Double-Layer Feature Fusion-Based Network Intrusion Detection System Using Convolutional Neural Network and Gated Recurrent Units[J]. Complex & Intelligent Systems, 2024, 10(3): 3353-3370. |
| [90] | ULLAH F, ULLAH S, SRIVASTAVA G, et al. IDS-INT: Intrusion Detection System Using Transformer-Based Transfer Learning for Imbalanced Network Traffic[J]. Digital Communications and Networks, 2024, 10(1): 190-204. |
| [91] | VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention Is All You Need[EB/OL]. (2023-08-02)[2025-04-05]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1706.03762. |
| [92] | CUI Susu, JIANG Bo, CAI Zhenzhen, et al. A Session-Packets-Based Encrypted Traffic Classification Using Capsule Neural Networks[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE 21st International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications; IEEE 17th International Conference on Smart City; IEEE 5th International Conference on Data Science and Systems. New York: IEEE, 2019: 429-436. |
| [93] | TIAN Qiuting, HAN Dezhi, LI Kuanching, et al. An Intrusion Detection Approach Based on Improved Deep Belief Network[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2020, 50: 3162-3178. |
| [94] | ZHAO Ziyi, GUO Yingya, WANG J H, et al. CL-ETC: A Contrastive Learning Method for Encrypted Traffic Classification[C]// IEEE. 2022 IFIP Networking Conference. New York: IEEE, 2022: 1-9. |
| [95] |
WANG Pan, CHEN Xuejiao. SAE-Based Encrypted Traffic Identification Method[J]. Computer Engineering, 2018, 44(11): 140-147, 153.
doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0052059 |
|
王攀, 陈雪娇. 基于堆栈式自动编码器的加密流量识别方法[J]. 计算机工程, 2018, 44(11):140-147,153.
doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0052059 |
|
| [96] | SNOUSSI R, YOUSSEF H. VAE-Based Latent Representations Learning for Botnet Detection in IoT Networks[EB/OL]. (2022-10-07)[2025-04-05]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10922-022-09690-4. |
| [97] | ALRAYES F S, ZAKARIAH M, AMIN S U, et al. Intrusion Detection in IoT Systems Using Denoising Autoencoder[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 122401-122425. |
| [98] | MIRSKY Y, DOITSHMAN T, ELOVICI Y, et al. Kitsune: An Ensemble of Autoencoders for Online Network Intrusion Detection[EB/OL]. (2018-05-27)[2025-04-05]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.09089. |
| [99] | CHENG A. PAC-GAN: Packet Generation of Network Traffic Using Generative Adversarial Networks[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE 10th Annual Information Technology, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference. New York: IEEE, 2019: 728-734. |
| [100] | GUO Yu, XIONG Gang, LI Zhen, et al. TA-GAN: GAN Based Traffic Augmentation for Imbalanced Network Traffic Classification[C]// IEEE. 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. New York: IEEE, 2021: 1-8. |
| [101] | ZHANG Rongqian, LUO Senlin, PAN Linin, et al. Generating Adversarial Examples via Enhancing Latent Spatial Features of Benign Traffic and Preserving Malicious Functions[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 490: 413-430. |
| [102] | ALDHAHERI S, ALHUZALI A. SGAN-IDS: Self-Attention-Based Generative Adversarial Network against Intrusion Detection Systems[EB/OL]. (2023-09-11)[2025-04-05]. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23187796. |
| [103] | HONG Yueping, LI Qi, YANG Yanqing, et al. Graph Based Encrypted Malicious Traffic Detection with Hybrid Analysis of Multi-View Features[EB/OL]. (2023-06-09)[2025-04-05]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2023.119229. |
| [104] | CHENG Jin, WU Yulei, E Yuepeng, et al. MATEC: A Lightweight Neural Network for Online Encrypted Traffic Classification[EB/OL]. (2021-09-21)[2025-04-05]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2021.108472. |
| [105] | DUY P T, KHOA N H, DO H H, et al. Investigating on the Robustness of Flow-Based Intrusion Detection System against Adversarial Samples Using Generative Adversarial Networks[EB/OL]. (2023-03-21)[2025-04-05]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jisa.2023.103472. |
| [106] | WANG Bin, GUO Yankai, QIAN Yaguan, et al. Defense of Traffic Classifiers Based on Convolutional Networks against Adversarial Examples[J]. Journal of Cyber Security, 2022, 7(1): 145-156. |
| [107] | CHERNIKOVA A, OPREA A. Fence: Feasible Evasion Attacks on Neural Networks in Constrained Environments[J]. ACM Transactions on Privacy and Security, 2022, 25(4): 1-34. |
| [108] | SHU Dule, LESLIE N O, KAMHOUA C A, et al. Generative Adversarial Attacks against Intrusion Detection Systems Using Active Learning[C]// ACM. The 2nd ACM Workshop on Wireless Security and Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2020: 1-6. |
| [109] | CHENG Qiumei, ZHOU Shiying, SHEN Yi, et al. Packet-Level Adversarial Network Traffic Crafting Using Sequence Generative Adversarial Networks[EB/OL]. (2023-03-31)[2025-04-05]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2103.04794. |
| [1] | JIN Zhigang, LI Zimeng, CHEN Xuyang, LIU Zepei. Review of Network Intrusion Detection System for Unbalanced Data [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(8): 1240-1253. |
| [2] | ZHANG Xinglan, TAO Kejin. Universal Perturbations Generation Method Based on High-Level Features and Important Channels [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(5): 767-777. |
| [3] | JIN Zengwang, JIANG Lingyang, DING Junyi, ZHANG Huixiang, ZHAO Bo, FANG Pengfei. A Review of Research on Industrial Control System Security [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(3): 341-363. |
| [4] | CHEN Hongsong, LIU Xinrui, TAO Zimei, WANG Zhiheng. A Survey of Anomaly Detection Model for Time Series Data Based on Deep Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(3): 364-391. |
| [5] | LI Hailong, CUI Zhian, SHEN Xieyang. Overview of Anomaly Analysis and Detection Methods for Network Traffic [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 194-214. |
| [6] | WU Haoying, CHEN Jie, LIU Jun. Improved Neural Network Differential Distinguisher of Simon32/64 and Simeck32/64 [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 249-259. |
| [7] | JIN Di, REN Hao, TANG Rui, CHEN Xingshu, WANG Haizhou. Research on Offensive Language Detection in Social Networks Based on Emotion-Assisted Multi-Task Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 281-294. |
| [8] | TAI Yingying, WEI Yuanyuan, ZHOU Hanxun, WANG Yan. Encrypted Traffic Classification Method Based on Optimal Transport and I-ELM [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(1): 148-158. |
| [9] | CHEN Xiaojing, TAO Yang, WU Baiqi, DIAO Yunfeng. Optimization Gradient Perception Adversarial Attack for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(9): 1386-1395. |
| [10] | XU Ruzhi, ZHANG Ning, LI Min, LI Zixuan. Research on a High Robust Detection Model for Malicious Software [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(8): 1184-1195. |
| [11] | TIAN Zhao, NIU Yajie, SHE Wei, LIU Wei. A Reputation Evaluation Method for Vehicle Nodes in V2X [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(5): 719-731. |
| [12] | ZHANG Guanghua, LIU Yichun, WANG He, HU Boning. Defense Scheme for Removing Deep Neural Network Backdoors Based on JSMA Adversarial Attacks [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(4): 545-554. |
| [13] | XU Zirong, GUO Yanping, YAN Qiao. Malicious Software Adversarial Defense Model Based on Feature Severity Ranking [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(4): 640-649. |
| [14] | YANG Zhipeng, LIU Daidong, YUAN Junyi, WEI Songjie. Research on Network Local Security Situation Fusion Method Based on Self-Attention Mechanism [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(3): 398-410. |
| [15] | JIANG Rong, LIU Haitian, LIU Cong. Unsupervised Network Intrusion Detection Method Based on Ensemble Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(3): 411-426. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||