Netinfo Security ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (5): 767-777.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.05.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
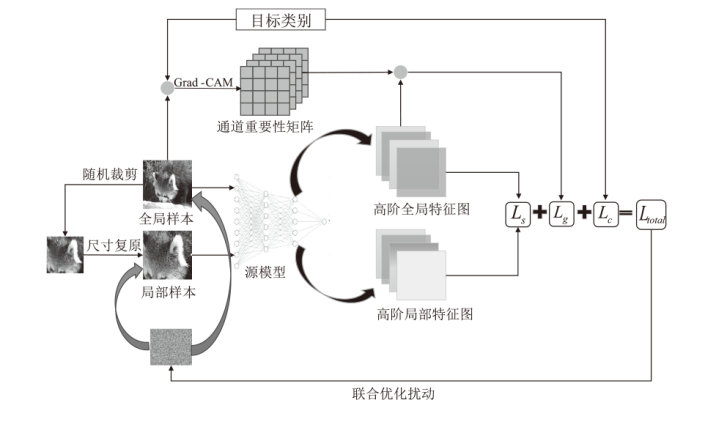
Universal Perturbations Generation Method Based on High-Level Features and Important Channels
- School of Computer Science, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100124, China
-
Received:2025-02-19Online:2025-05-10Published:2025-06-10
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHANG Xinglan, TAO Kejin. Universal Perturbations Generation Method Based on High-Level Features and Important Channels[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(5): 767-777.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://netinfo-security.org/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.05.009
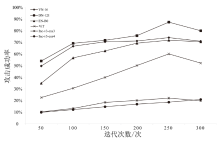
| 方法 | VN-16 | DN-121 | EN-B0 | ViT | Inc-v3-ens3 | Inc-v3-ens4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGSM | 20.5% | 30.5% | 19.8% | 11.2% | 6.2% | 5.0% |
| BIM | 27.3% | 36.6% | 25.3% | 14.3% | 10.3% | 11.2% |
| MI-FGSM | 47.8% | 50.7% | 33.6% | 22.8% | 17.3% | 15.7% |
| SGM | 55.9% | 63.0% | 58.7% | 44.7% | 12.3% | 10.9% |
| BN-MI-FGSM | 61.4% | 64.2% | 62.5% | 49.6% | 16.2% | 15.1% |
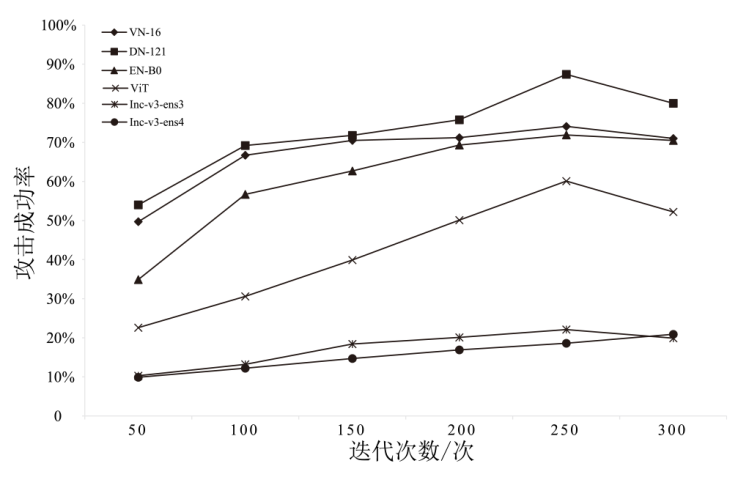
| 本文方法 | 74.1% | 87.4% | 71.9% | 60.1% | 22.1% | 20.9% |
| 方法 | VN-16 | DN-121 | EN-B0 | ViT | Inc-v3-ens3 | Inc-v3-ens4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGSM | 13.6% | 28.5% | 14.7% | 10.6% | 14.2% | 13.5% |
| BIM | 18.6% | 37.6% | 21.6% | 13.3% | 27.3% | 22.3% |
| MI-FGSM | 43.2% | 49.0% | 39.8% | 34.2% | 22.7% | 27.8% |
| SGM | 56.0% | 55.1% | 54.3% | 45.7% | 29.0% | 26.4% |
| BN-MI-FGSM | 65.3% | 67.7% | 50.6% | 60.4% | 31.4% | 25.9% |
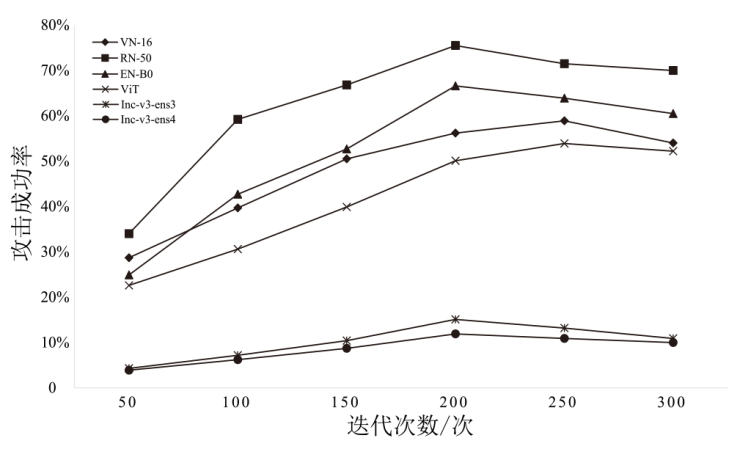
| 本文方法 | 72.7% | 84.8% | 75.3% | 61.7% | 30.8% | 30.9% |
| [1] | ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I, VINYALS O. Recurrent Neural Network Regularization[EB/OL].(2015-02-19)[2024-12-24]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.2329v5. |
| [2] | HINTON G, DENG Li, YU Dong, et al. Deep Neural Networks for Acoustic Modeling in Speech Recognition: The Shared Views of Four Research Groups[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2012, 29(6): 82-97. |
| [3] | SUN Ke, XIAO Bin, LIU Dong, et al. Deep High-Resolution Representation Learning for Human Pose Estimation[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2019: 5686-5696. |
| [4] | ZHANG Yuqing, DONG Ying, LIU Caiyun, et al. Situation, Trends and Prospects of Deep Learning Applied to Cyberspace Security[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2018, 55(6): 1117-1142. |
| [5] | NAUMOV M, MUDIGERE D, SHI H M, et al. Deep Learning Recommendation Model for Personalization and Recommendation Systems[EB/OL].(2019-05-31)[2024-12-24]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.00091v1. |
| [6] | KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90. |
| [7] | SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition[EB/OL].(2015-04-10)[2024-12-24]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556v6. |
| [8] | SZEGEDY C, VANHOUCKE V, IOFFE S, et al. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2016: 2818-2826. |
| [9] | HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition[C]// IEEE. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2016: 770-778. |
| [10] | SZEGEDY C, ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I, et al. Intriguing Properties of Neural Networks[EB/OL].(2014-02-19)[2024-12-24]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.6199v4. |
| [11] | LONG Teng, GAO Qi, XU Lili, et al. A Survey on Adversarial Attacks in Computer Vision: Taxonomy, Visualization and Future Directions[EB/OL].(2022-07-27)[2024-12-24]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2022.102847. |
| [12] | GOODFELLOW I J, SHLENS J, SZEGEDY C, et al. Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples[EB/OL].(2015-03-20)[2024-12-24]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6572v3. |
| [13] | KURAKIN A, GOODFELLOW I J, BENGIO S. Adversarial Examples in the Physical World[EB/OL].(2017-02-11)[2024-12-24]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1607.02533. |
| [14] | DONG Yinpeng, LIAO Fangzhou, PANG Tianyu, et al. Boosting Adversarial Attacks with Momentum[C]// IEEE. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2018: 9185-9193. |
| [15] | CARLINI N, WAGNER D. Towards Evaluating the Robustness of Neural Networks[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York: IEEE, 2017: 39-57. |
| [16] | XIE Cihang, ZHANG Zhishuai, ZHOU Yuyin, et al. Improving Transferability of Adversarial Examples with Input Diversity[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2019: 2725-2734. |
| [17] | DONG Yinpeng, PANG Tianyu, SU Hang, et al. Evading Defenses to Transferable Adversarial Examples by Translation-Invariant Attacks[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2019: 4307-4316. |
| [18] | LIN Jiadong, SONG Chuanbiao, HE Kun, et al. Nesterov Accelerated Gradient and Scale Invariance for Adversarial Attacks[EB/OL].(2020-02-03)[2024-12-24]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.06281v5. |
| [19] | WEI Zhipeng, CHEN Jingjing, WU Zuxuan, et al. Enhancing the Self-Universality for Transferable Targeted Attacks[C]// IEEE. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2023: 12281-12290. |
| [20] | ZHANG Chaoning, BENZ P, IMTIAZ T, et al. Understanding Adversarial Examples from the Mutual Influence of Images and Perturbations[C]// IEEE. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2020: 14509-14518. |
| [21] | WU Dongxian, WANG Yisen, XIA Shutao, et al. Skip Connections Matter: On the Transferability of Adversarial Examples Generated with ResNets[EB/OL].(2020-02-14)[2024-12-24]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.05990v1. |
| [22] | BENZ P, ZHANG Chaoning, KWEON I S. Batch Normalization Increases Adversarial Vulnerability and Decreases Adversarial Transferability: A Non-Robust Feature Perspective[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). New York: IEEE, 2021: 7798-7807. |
| [23] | JANDIAL S, MANGLA P, VARSHNEY S, et al. AdvGAN: Harnessing Latent Layers for Adversary Generation[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW). New York: IEEE, 2019: 2045-2048. |
| [24] | ZHANG Qilong, LI Xiaodan, CHEN Yuefeng, et al. Beyond ImageNet Attack: Towards Crafting Adversarial Examples for Black-Box Domains[EB/OL].(2022-03-14)[2024-12-24]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.11528v4. |
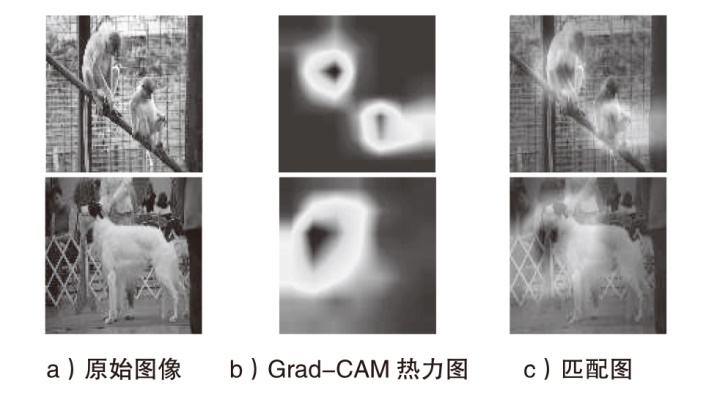
| [25] | SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(2): 336-359. |
| [26] | LI Xiang, GUO Haiwang, DENG Xinyang, et al. CGN: Class Gradient Network for the Construction of Adversarial Samples[EB/OL].(2023-11-07)[2024-12-24]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2023.119855. |
| [27] | DENG Jia, DONG Wei, SOCHER R, et al. ImageNet: A Large-Scale Hierarchical Image Database[C]// IEEE. 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2009: 248-255. |
| [28] | XIAO Han, RASUL K, VOLLGRAF R. Fashion-MNIST: A Novel Image Dataset for Benchmarking Machine Learning Algorithms[EB/OL].(2017-09-15)[2024-12-24]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.07747v2. |
| [29] | HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN D M L, et al. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York: IEEE, 2017: 2261-2269. |
| [30] | TAN Mingxing, LE Q V. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks[EB/OL].(2020-09-11)[2024-12-24]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.11946v5. |
| [31] | DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An Image is Worth 16×16 Words:Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale[EB/OL]. (2021-06-03)[2024-12-24]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929. |
| [32] | TRAMÈR F, KURAKIN A, PAPERNOT N, et al. Ensemble Adversarial Training: Attacks and Defenses[EB/OL]. (2020-04-26)[2024-12-24]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.07204v5. |
| [1] | JIN Zengwang, JIANG Lingyang, DING Junyi, ZHANG Huixiang, ZHAO Bo, FANG Pengfei. A Review of Research on Industrial Control System Security [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(3): 341-363. |
| [2] | CHEN Hongsong, LIU Xinrui, TAO Zimei, WANG Zhiheng. A Survey of Anomaly Detection Model for Time Series Data Based on Deep Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(3): 364-391. |
| [3] | LI Hailong, CUI Zhian, SHEN Xieyang. Overview of Anomaly Analysis and Detection Methods for Network Traffic [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 194-214. |
| [4] | WU Haoying, CHEN Jie, LIU Jun. Improved Neural Network Differential Distinguisher of Simon32/64 and Simeck32/64 [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 249-259. |
| [5] | JIN Di, REN Hao, TANG Rui, CHEN Xingshu, WANG Haizhou. Research on Offensive Language Detection in Social Networks Based on Emotion-Assisted Multi-Task Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(2): 281-294. |
| [6] | CHEN Xiaojing, TAO Yang, WU Baiqi, DIAO Yunfeng. Optimization Gradient Perception Adversarial Attack for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(9): 1386-1395. |
| [7] | XU Ruzhi, ZHANG Ning, LI Min, LI Zixuan. Research on a High Robust Detection Model for Malicious Software [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(8): 1184-1195. |
| [8] | TIAN Zhao, NIU Yajie, SHE Wei, LIU Wei. A Reputation Evaluation Method for Vehicle Nodes in V2X [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(5): 719-731. |
| [9] | ZHANG Guanghua, LIU Yichun, WANG He, HU Boning. Defense Scheme for Removing Deep Neural Network Backdoors Based on JSMA Adversarial Attacks [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(4): 545-554. |
| [10] | XU Zirong, GUO Yanping, YAN Qiao. Malicious Software Adversarial Defense Model Based on Feature Severity Ranking [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(4): 640-649. |
| [11] | YANG Zhipeng, LIU Daidong, YUAN Junyi, WEI Songjie. Research on Network Local Security Situation Fusion Method Based on Self-Attention Mechanism [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(3): 398-410. |
| [12] | JIANG Rong, LIU Haitian, LIU Cong. Unsupervised Network Intrusion Detection Method Based on Ensemble Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(3): 411-426. |
| [13] | FENG Guangsheng, JIANG Shunpeng, HU Xianlang, MA Mingyu. New Research Progress on Intrusion Detection Techniques for the Internet of Things [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(2): 167-178. |
| [14] | ZHAO Pengcheng, YU Junqing, LI Dong. An Optimal Algorithm for Traffic Scheduling in SRv6 Network Based on Deep Learning [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(2): 272-281. |
| [15] | JIN Zhigang, DING Yu, WU Xiaodong. Federated Intrusion Detection Algorithm with Bilateral Correction Merging Gradient Difference [J]. Netinfo Security, 2024, 24(2): 293-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||