信息网络安全 ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (11): 1762-1773.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.11.009
基于可信执行环境的联邦学习分层动态防护算法
王亚杰1, 陆锦标1, 李宇航1, 范青2, 张子剑1( ), 祝烈煌1
), 祝烈煌1
1.北京理工大学网络空间安全学院 北京 100081 2.华北电力大学控制与计算机工程学院 北京 102206
-
收稿日期:2025-07-27出版日期:2025-11-10发布日期:2025-12-02 -
通讯作者:张子剑wangyajie19@bit.edu.cn -
作者简介:王亚杰(1993—),男,河北,助理研究员,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为人工智能安全、数据安全与隐私保护|陆锦标(2002—),男,广东,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为人工智能安全、隐私保护|李宇航(2002—),男,江苏,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为人工智能安全、隐私保护|范青(1996—),女,山东,副教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为应用密码学、信息安全与安全协议设计|张子剑(1984—),男,北京,教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为区块链安全、通信安全、数据隐私|祝烈煌(1976—),男,浙江,教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为密码算法及安全协议、区块链技术、云计算安全、大数据隐私保护 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2023YFF0905300)
Hierarchical Dynamic Protection Algorithm for Federated Learning Based on Trusted Execution Environment
WANG Yajie1, LU Jinbiao1, LI Yuhang1, FAN Qing2, ZHANG Zijian1( ), ZHU Liehuang1
), ZHU Liehuang1
1. School of Cyberspace Science and Technology ,Beijing Institute of Technology Beijing 100081, China 2. School of Control and Computer Engineering ,North China Electric Power University Beijing 102206, China
-
Received:2025-07-27Online:2025-11-10Published:2025-12-02
摘要:
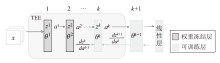
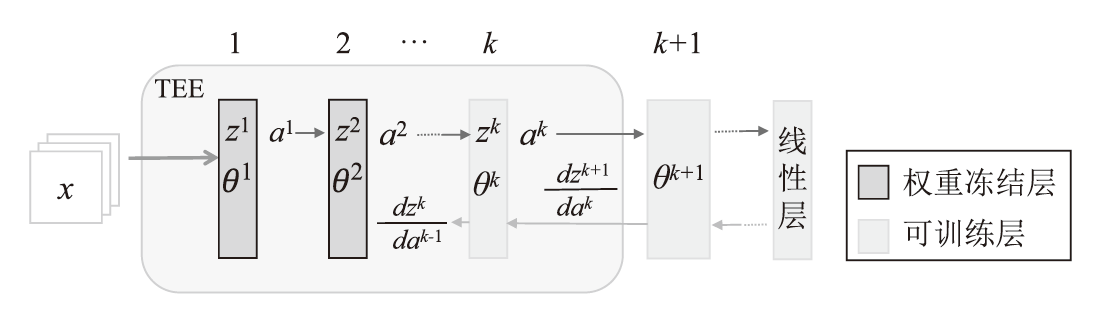
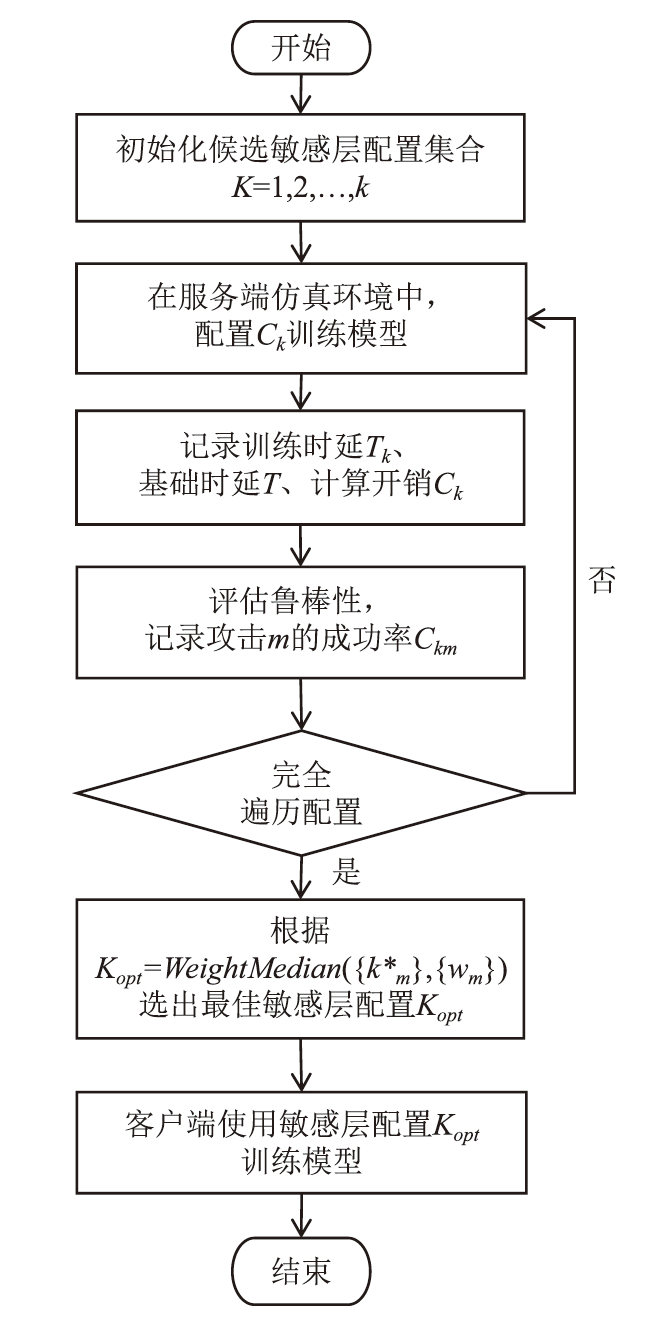
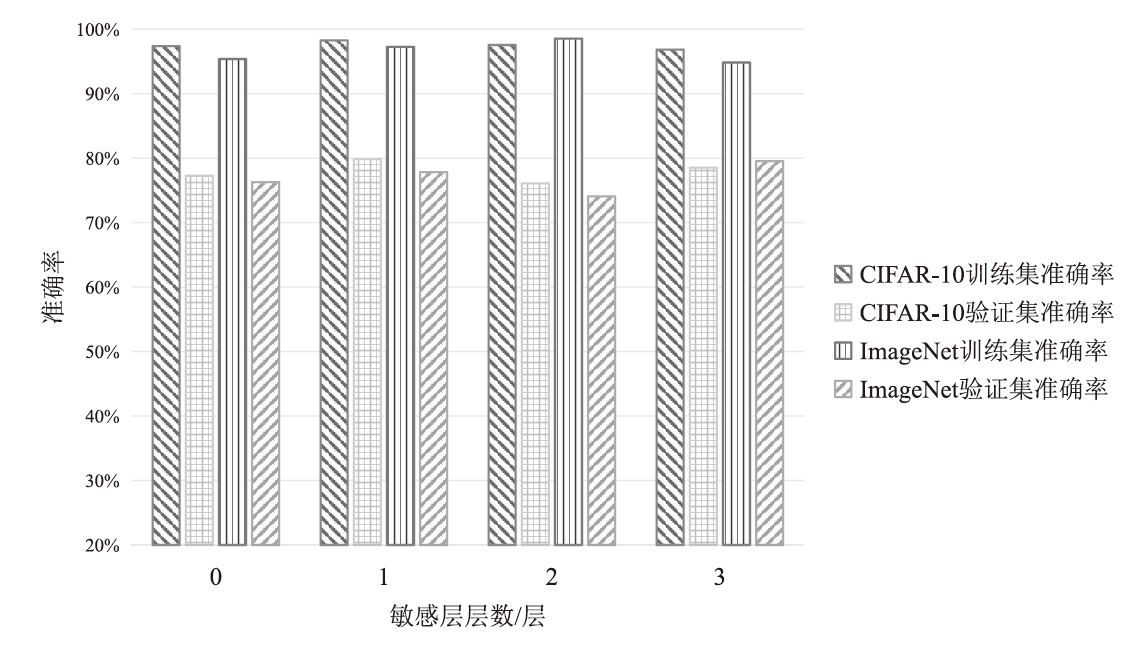
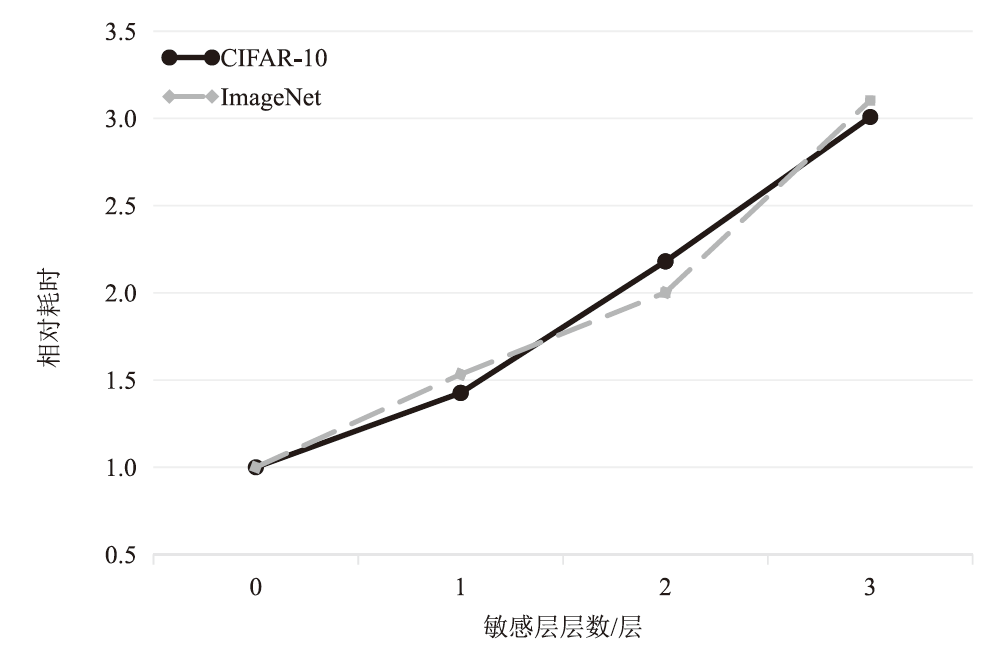
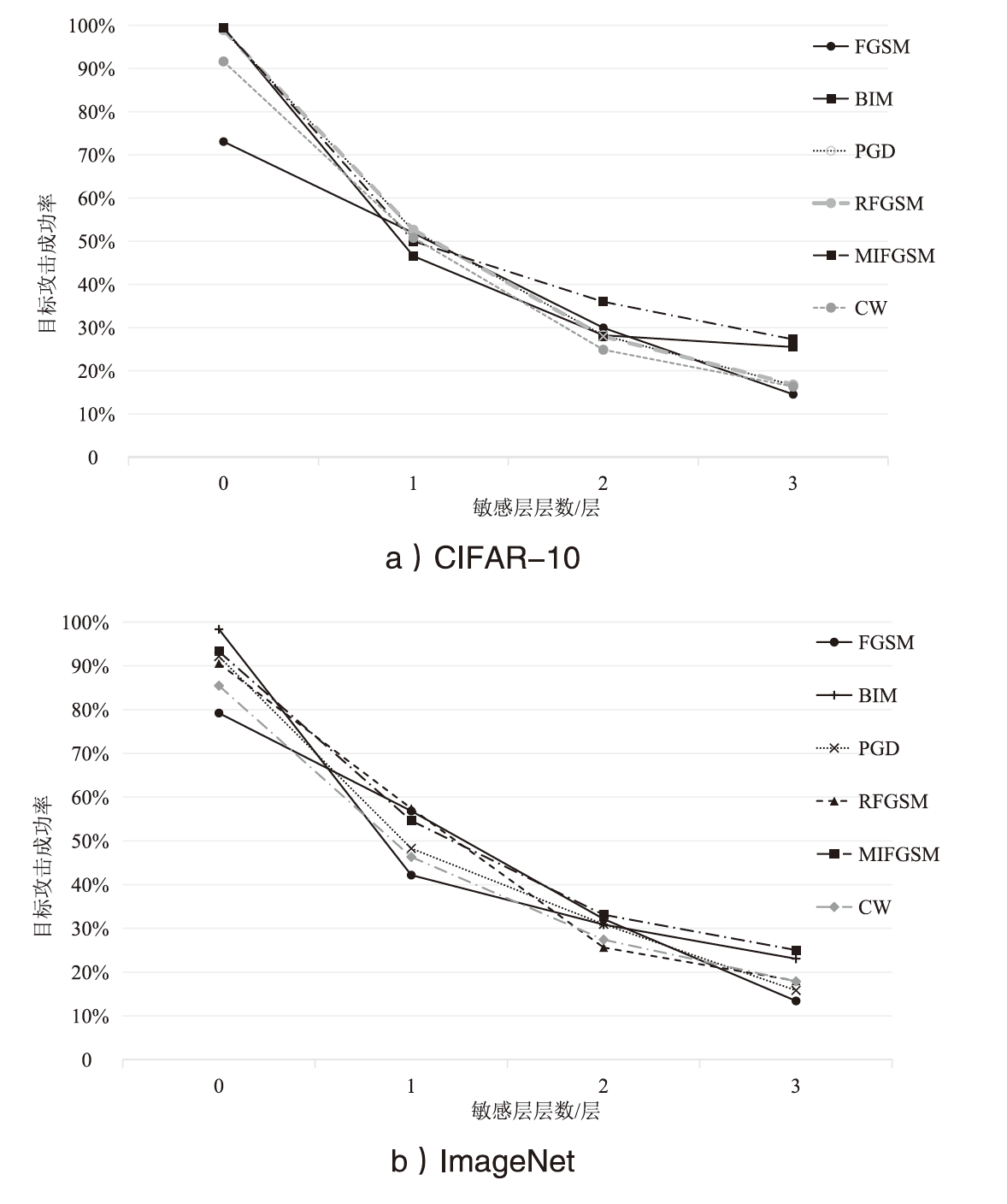
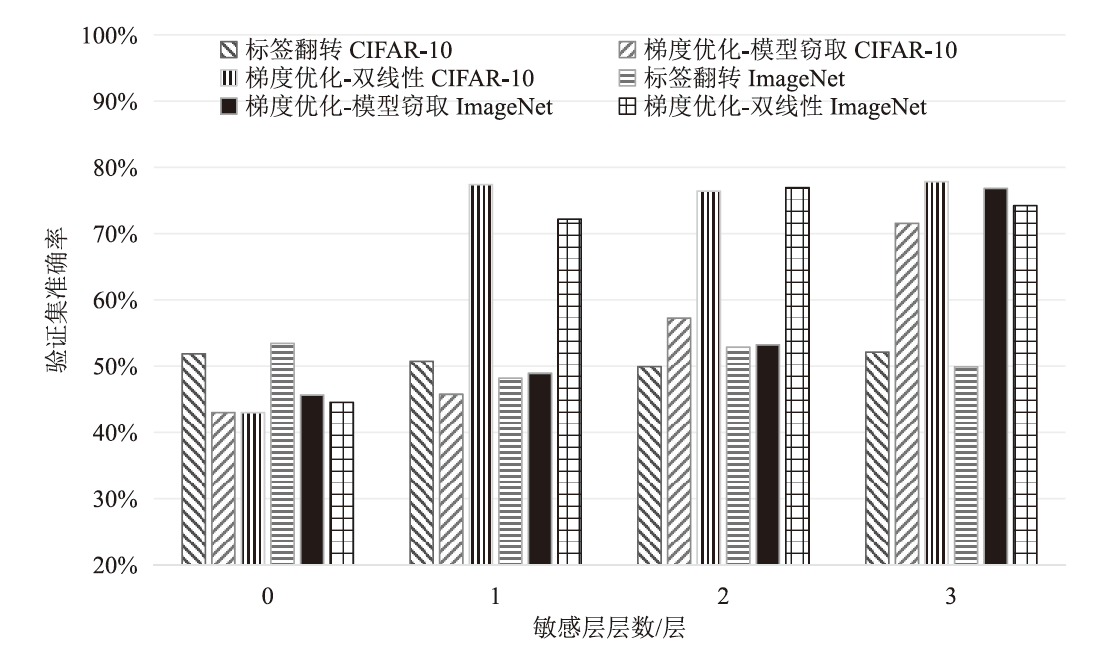
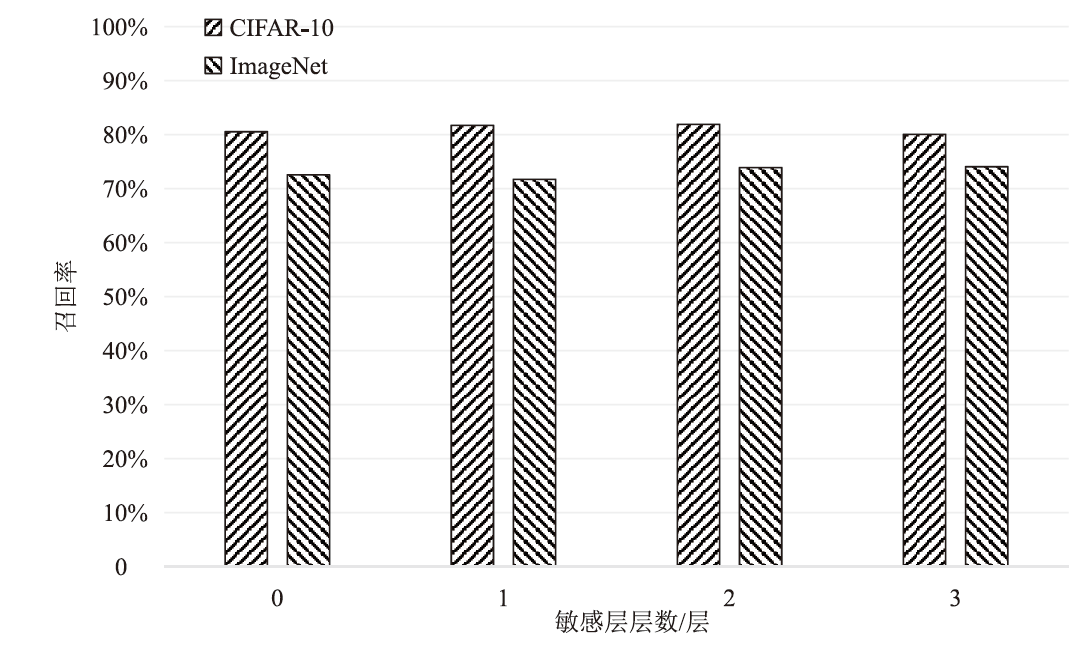
在现有联邦学习隐私保护方案中,基于硬件的可信执行环境(TEE)由于其高效且安全的特性,逐渐成为新的范式。然而,受限于硬件条件,TEE保护层数过多,训练效率会急剧下降;TEE保护层数过少,则难以充分保障隐私安全。针对此问题,文章提出一种基于可信执行环境的联邦学习分层动态防护算法。该算法在服务端设计敏感层动态选择机制,通过逐层贪婪训练法实现内存受限环境下的安全参数优化,结合对抗鲁棒性评估模型量化不同敏感层配置的防御效能,据此确定需保护的敏感层;在客户端通过分层可信训练机制,采用双通道参数聚合实现敏感层与非敏感层的差异化训练。实验结果表明,分层防护算法能够有效阻断特征语义的连贯性,使得替代模型的决策边界与原始模型产生系统性偏差。在抵御多种对抗攻击方面,文章算法能够显著降低目标攻击的效果,降幅可达82%以上。此外,文章验证了该算法对数据投毒攻击的防御效能,在梯度投毒场景下,模型的准确率可提升35%以上。
中图分类号:
引用本文
王亚杰, 陆锦标, 李宇航, 范青, 张子剑, 祝烈煌. 基于可信执行环境的联邦学习分层动态防护算法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(11): 1762-1773.
WANG Yajie, LU Jinbiao, LI Yuhang, FAN Qing, ZHANG Zijian, ZHU Liehuang. Hierarchical Dynamic Protection Algorithm for Federated Learning Based on Trusted Execution Environment[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(11): 1762-1773.
| [1] | HAGESTEDT I, ZHANG Yang, HUMBERT M, et al. MBeacon: Privacy-Preserving Beacons for DNA Methylation Data[EB/OL]. [2025-07-20]. https://www.ndss-symposium.org/ndss-paper/mbeacon-privacy-preserving-beacons-for-dna-methylation-data/. |
| [2] | MCMAHAN B, MOORE E, RAMAGE D, et al. Communication-Efficient Learning of Deep Networks from Decentralized Data[C]// PMLR. The 20th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. New York: PMLR, 2017: 1273-1282. |
| [3] | LIU Zhentao, LI Han, WU Lang, et al. Medical Data Sharing and Privacy Protection Based on Federated Learning[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2024, 45(9): 2577-2583. |
| 刘振涛, 李涵, 吴浪, 等. 基于联邦学习的医疗数据共享与隐私保护[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2024, 45(9):2577-2583. | |
| [4] | AYEELYAN J, UTOMO S, ROUMIYAR A, et al. Federated Learning Design and Functional Models: Survey[EB/OL]. (2024-11-06)[2025-07-20]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-024-10969-y. |
| [5] | LATIF N, MA Wenping, AHMAD H B. Advancements in Securing Federated Learning with IDS: A Comprehensive Review of Neural Networks and Feature Engineering Techniques for Malicious Client Detection[EB/OL]. (2025-01-13)[2025-07-20]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-024-11082-w. |
| [6] | NGUYEN G T, DIAZ J S, CALATRAVA A, et al. Landscape of Machine Learning Evolution: Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning Frameworks and Tools[EB/OL]. (2024-12-20)[2025-07-20]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-024-11036-2. |
| [7] | SHENOY D, BHAT R, PRAKASHA K K. Exploring Privacy Mechanisms and Metrics in Federated Learning[EB/OL]. (2025-05-03)[2025-07-20]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-025-11170-5. |
| [8] | YUAN Jiangjun, LIU Weinan, SHI Jiawen, et al. Approximate Homomorphic Encryption Based Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning: A Survey[EB/OL]. (2025-01-06)[2025-07-20]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-024-11076-8. |
| [9] | DWORK C, ROTH A. The Algorithmic Foundations of Differential Privacy[J]. Foundations and Trends® in Theoretical Computer Science, 2014, 9(3-4): 211-407. |
| [10] | GAO Hongfeng, HUANG Hao, TIAN Youliang. Secure Byzantine Resilient Federated Learning Based on Multi-Party Computation[J]. Journal on Communications, 2025, 46(2): 108-122. |
| 高鸿峰, 黄浩, 田有亮. 基于多方计算的安全拜占庭弹性联邦学习[J]. 通信学报, 2025, 46(2):108-122. | |
| [11] |
ZHANG Han, YU Hang, ZHOU Jiwei, et al. Survey on Trusted Execution Environment Towards Privacy Computing[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2025, 45(2): 467-481.
doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2024020222 |
|
张涵, 于航, 周继威, 等. 面向隐私计算的可信执行环境综述[J]. 计算机应用, 2025, 45(2):467-481.
doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2024020222 |
|
| [12] | ZHANG Fengwei, ZHOU Lei, ZHANG Yiming, et al. Trusted Execution Environment: State-of-the-Art and Future Directions[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2024, 61(1): 243-260. |
| 张锋巍, 周雷, 张一鸣, 等. 可信执行环境:现状与展望[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2024, 61(1):243-260. | |
| [13] | CAO Yihao, ZHANG Jianbiao, ZHAO Yaru, et al. SRFL: A Secure & Robust Federated Learning Framework for IoT with Trusted Execution Environments[EB/OL]. (2023-09-09)[2025-07-20]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.122410. |
| [14] | MO Fan, HADDADI H, KATEVAS K, et al. PPFL: Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning with Trusted Execution Environments[C]//ACM. MobiSys’21: The 19th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services. New York: ACM, 2021: 94-108. |
| [15] | QUEYRUT S, SCHIAVONI V, FELBER P. Mitigating Adversarial Attacks in Federated Learning with Trusted Execution Environments[C]// IEEE. 2023 IEEE 43rd International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems. New York: IEEE, 2023: 626-637. |
| [16] | MONDAL A, MORE Y, ROOPARAGHUNATH R H, et al. Poster: FLATEE: Federated Learning Across Trusted Execution Environments[C]// IEEE. IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy(EuroS&P 2021). New York: IEEE, 2021: 707-709. |
| [17] |
KATO F, CAO Yang, YOSHIKAWA M. Olive: Oblivious Federated Learning on Trusted Execution Environment against the Risk of Sparsification[J]. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 2023, 16(10): 2404-2417.
doi: 10.14778/3603581.3603583 URL |
| [18] | ZHANG Yuhui, WANG Zhiwei, CAO Jiangfeng, et al. ShuffleFL: Gradient-Preserving Federated Learning Using Trusted Execution Environment[C]// ACM. ACM International Conference on Computing Frontiers 2021. New York:ACM, 2021: 161-168. |
| [1] | 陈先意, 汪学波, 崔琦, 付章杰, 王茜茜, 曾一福. 面向个性化联邦学习的后门攻击与防御综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1418-1438. |
| [2] | 拾以娟, 周丹平, 范磊, 刘茵. 基于可信执行环境的安全多方计算协议[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(9): 1439-1446. |
| [3] | 荀毅杰, 崔嘉容, 毛伯敏, 秦俊蔓. 基于联邦学习的智能汽车CAN总线入侵检测系统[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(6): 872-888. |
| [4] | 邓东上, 王伟业, 张卫东, 吴宣够. 基于模型特征方向的分层个性化联邦学习框架[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(6): 889-897. |
| [5] | 朱率率, 刘科乾. 基于掩码的选择性联邦蒸馏方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(6): 920-932. |
| [6] | 赵锋, 范淞, 赵艳琦, 陈谦. 基于本地差分隐私的可穿戴医疗设备流数据隐私保护方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(5): 700-712. |
| [7] | 秦金磊, 康毅敏, 李整. 智能电网中轻量级细粒度的多维多子集隐私保护数据聚合[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(5): 747-757. |
| [8] | 胡宇涵, 杨高, 蔡红叶, 付俊松. 三维分布式无线智能系统数据传输路径隐私保护方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(4): 536-549. |
| [9] | 何可, 王建华, 于丹, 陈永乐. 基于自适应采样的机器遗忘方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(4): 630-639. |
| [10] | 李佳东, 曾海涛, 彭莉, 汪晓丁. 一种保护数据隐私的匿名路由联邦学习框架[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(3): 494-503. |
| [11] | 郝萌, 李佳勇, 杨洪伟, 张伟哲. 异构CPU-GPU系统机密计算综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(11): 1658-1672. |
| [12] | 关志, 胡建斌, 李悦, 陈钟. 基于可信执行环境的区块链技术与应用综述[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(11): 1673-1690. |
| [13] | 薛开平, 张淳一, 柳枫, 王峰. 基于可信执行环境的加密数据库索引安全增强方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(11): 1718-1731. |
| [14] | 赵波, 吕佳敏, 王一琁. 一种面向容器生命周期的多维安全度量架构[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(11): 1745-1761. |
| [15] | 卢笛, 刘玉佳, 吕超越, 孙梦娜, 张清文, 杨力. 一种云原生TEE服务共享机制[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(11): 1774-1791. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||