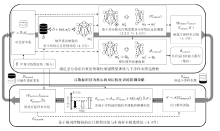
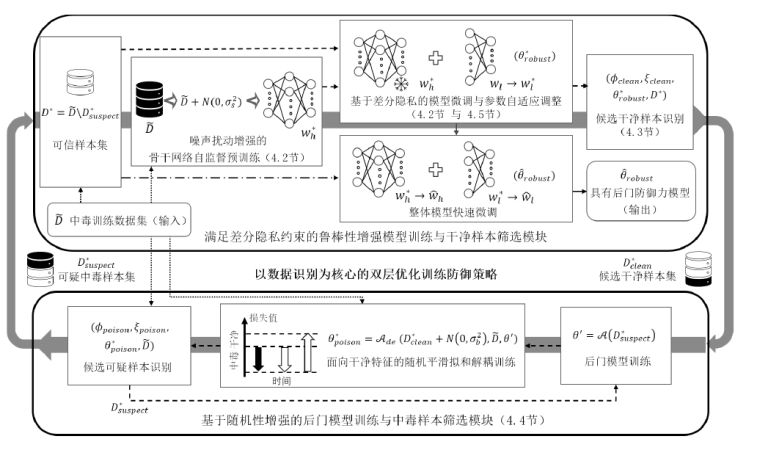
信息网络安全 ›› 2025, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (7): 1074-1091.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1122.2025.07.007
面向数据投毒后门攻击的随机性增强双层优化防御方法
闫宇坤1,2, 唐朋3, 陈睿1,2( ), 都若尘1,2, 韩启龙1,2
), 都若尘1,2, 韩启龙1,2
- 1.哈尔滨工程大学计算机科学与技术学院,哈尔滨150001
2.电子政务建模与仿真国家工程实验室,哈尔滨 150001
3.山东大学网络空间安全学院,青岛 266237
-
收稿日期:2025-05-07出版日期:2025-07-10发布日期:2025-08-07 -
通讯作者:陈睿 E-mail:ruichen@hrbeu.edu.cn -
作者简介:闫宇坤(1997—),男,河北,博士研究生,CCF会员,主要研究方向为数据安全和隐私保护|唐朋(1987—),男,山东,副教授,博士,主要研究方向为数据安全和隐私保护|陈睿(1983—),男,四川,教授,博士,主要研究方向为数据安全和隐私保护|都若尘(1996—),男,黑龙江,博士研究生,CCF会员,主要研究方向为数据投毒后门防御|韩启龙(1974—),男,黑龙江,教授,博士,CCF会员,主要研究方向为数据安全和隐私保护 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(62002203);黑龙江省重点研发计划(GA23A915)
A Randomness Enhanced Bi-Level Optimization Defense Method against Data Poisoning Backdoor Attacks
YAN Yukun1,2, TANG Peng3, CHEN Rui1,2( ), DU Ruochen1,2, HAN Qilong1,2
), DU Ruochen1,2, HAN Qilong1,2
- 1. College of Computer Science and Technology, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
2. National Engineering Laboratory for Modeling and Emulation in E-Government, Harbin 150001, China
3. School of Cyber Science and Technology, Shandong University, Qingdao 266237, China
-
Received:2025-05-07Online:2025-07-10Published:2025-08-07 -
Contact:CHEN Rui E-mail:ruichen@hrbeu.edu.cn
摘要:
数据投毒后门攻击揭示了深度神经网络在安全性方面的脆弱性,严重威胁其在实际应用中的可靠性。尽管已有多种防御策略被提出,但在实际部署中仍面临两大挑战:1)过度依赖于有关攻击者行为或训练数据的先验知识,导致泛化性受限;2)难以在模型性能与防御能力之间取得有效平衡。因此,文章提出一种面向数据投毒后门攻击的随机性增强双层优化防御框架(RADAR)。该框架以数据识别为核心,将鲁棒性增强训练与样本筛选机制有机融合,无需任何先验信息,即可在模型训练过程中动态识别数据集内干净样本与可疑中毒样本,并在筛选所得可信数据上进行模型快速调整,构建具备稳健防御能力的深度神经网络。具体而言,RADAR结合噪声增强的自监督预训练与满足差分隐私约束的参数自适应微调机制,即使在中毒样本主导目标类别的极端情况下,也能识别其为全局异常并抑制拟和,保障干净样本的准确筛选。此外,RADAR设计了面向干净特征的随机平滑拟和解耦策略,在干净样本受限条件下,有效去除后门模型对干净特征的拟和能力,从而降低可疑中毒样本识别的假阳率。通过在多种类型数据投毒后门攻击下开展防御实验,结果表明RADAR不仅在干净样本上分类性能优良,还展现出优异的防御能力,将各类攻击成功率抑制在7%以下,体现出良好的安全性与实用性。
中图分类号:
引用本文
闫宇坤, 唐朋, 陈睿, 都若尘, 韩启龙. 面向数据投毒后门攻击的随机性增强双层优化防御方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(7): 1074-1091.
YAN Yukun, TANG Peng, CHEN Rui, DU Ruochen, HAN Qilong. A Randomness Enhanced Bi-Level Optimization Defense Method against Data Poisoning Backdoor Attacks[J]. Netinfo Security, 2025, 25(7): 1074-1091.
表1
部分符号说明
| 符号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 原始干净数据集 | |
| 中毒数据集 | |
| 中毒数据集内干净子集 | |
| 中毒数据集内中毒子集 | |
| 粗筛候选干净样本集 | |
| 精筛候选干净样本集 | |
| 可疑中毒样本集 | |
| 可信样本集 | |
| 正常模型训练方法 | |
| 鲁棒性增强模型训练方法 | |
| 只拟和后门特征的模型训练方法 | |
| 面向干净特征的拟和解耦训练方法 | |
| DNN模型参数 | |
| 后门模型参数 | |
| 仅执行若干轮次训练的后门模型参数 | |
| 仅拟和后门特征的模型参数 | |
| 鲁棒性增强模型参数 | |
| 具有后门防御力的模型参数 | |
| 线性预测层参数 | |
| 骨干网络参数 | |
| 经过自监督预训练的骨干网络参数 |
表3
RADAR与中毒样本筛选方法在TPR和FPR上的对比
| 方法 | 均值 | SS | AC | SCAn | CT | RADAR | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C I F A R - 10 | TPR (%) | FPR (%) | TPR (%) | FPR (%) | TPR (%) | FPR (%) | TPR (%) | FPR (%) | TPR (%) | FPR (%) | |
| No Poison | — | 15.02 | — | 3.13 | — | 2.42 | — | 2.2 | — | 1.33 | |
| BadNets | 100 | 14.14 | 100 | 3.09 | 100 | 0.30 | 100 | 0.06 | 100 | 1.23 | |
| Blend | 93.40 | 14.20 | 0.00 | 3.25 | 96.0 | 3.38 | 99.40 | 1.15 | 99.42 | 1.20 | |
| Trojan | 22.20 | 14.93 | 0.00 | 2.14 | 100 | 0.02 | 100 | 0.45 | 100 | 0.37 | |
| CL | 90.10 | 14.24 | 100 | 2.80 | 100 | 2.76 | 100 | 0.02 | 100 | 0.75 | |
| SIG | 0.00 | 15.15 | 0.00 | 5.11 | 96.60 | 7.78 | 100 | 0.51 | 100 | 0.69 | |
| Dynamic | 99.00 | 14.15 | 99.0 | 2.13 | 98.00 | 3.42 | 100 | 0.14 | 100 | 0.51 | |
| TaCT | 73.60 | 14.41 | 0.00 | 2.02 | 100 | 3.52 | 100 | 0.48 | 100 | 3.56 | |
| Adap-patch | 70.40 | 14.44 | 0.00 | 5.91 | 97.40 | 2.06 | 99.03 | 0.41 | 93.2 | 0.43 | |
| Adap-blend | 89.00 | 14.25 | 0.00 | 2.37 | 0.00 | 2.51 | 100 | 0.73 | 97.0 | 1.56 | |
| Average | 70.86 | 14.49 | 33.22 | 3.19 | 87.56 | 2.82 | 99.82 | 0.62 | 98.85 | 1.16 | |
| G T S R B | No Poison | — | 39.13 | — | 5.78 | — | 2.13 | — | 0.55 | — | 3.23 |
| BadNets | 92.85 | 38.41 | 89.11 | 5.44 | 87.22 | 38.41 | 100 | 0.01 | 100 | 2.26 | |
| Blend | 93.99 | 38.39 | 99.25 | 76.09 | 93.99 | 0.03 | 100 | 0.16 | 100 | 1.01 | |
| Trojan | 99.25 | 38.34 | 99.25 | 5.28 | 100 | 0.01 | 100 | 0.52 | 100 | 0.09 | |
| SIG | 65.04 | 38.85 | 0.00 | 10.76 | 61.28 | 0.00 | 100 | 1.57 | 100 | 3.87 | |
| Dynamic | 89.11 | 38.44 | 77.82 | 10.52 | 74.81 | 0.00 | 100 | 1.15 | 100 | 0.22 | |
| TaCT | 90.60 | 38.57 | 0.00 | 5.02 | 98.87 | 0.00 | 100 | 0.24 | 100 | 5.85 | |
| Adap-patch | 51.13 | 38.83 | 0.00 | 5.76 | 4.89 | 1.69 | 90.23 | 1.02 | 86.84 | 4.73 | |
| Adap-blend | 36.84 | 38.97 | 0.00 | 6.08 | 97.4 | 2.98 | 100 | 1.36 | 95.86 | 5.83 | |
| Average | 77.35 | 38.66 | 46.68 | 14.53 | 77.31 | 5.03 | 98.78 | 0.73 | 97.83 | 2.71 | |
表4
RADAR与其他防御方法性能对比
| 方法 | 均值 | No Defense | SS | AC | SCAn | NC | ABL | NAD | DBD | ASD | CT | RADAR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
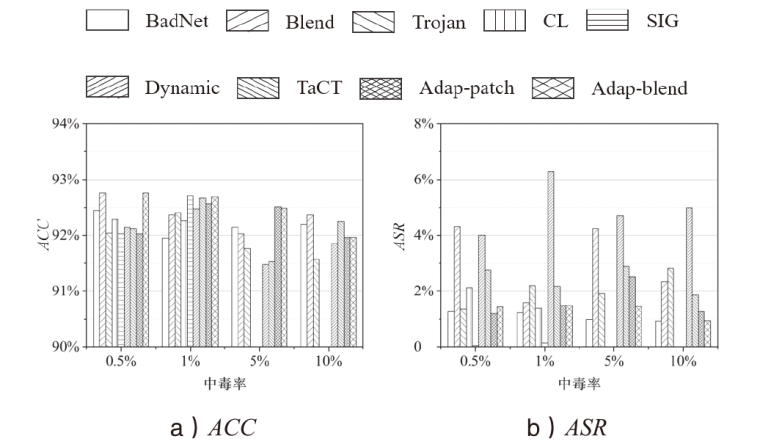
| C I F A R - 10 | BadNets | ACC(%) | 93.81 | 92.97 | 92.20 | 93.90 | 93.77 | 89.63 | 85.26 | 86.77 | 92.91 | 93.88 | 91.95 |
| ASR(%) | 100 | 0.69 | 0.75 | 0.66 | 0.91 | 100 | 1.81 | 1.94 | 100 | 0.61 | 1.23 | ||
| Blend | ACC(%) | 93.98 | 92.51 | 91.41 | 93.27 | 93.47 | 84.13 | 86.46 | 84.65 | 93.07 | 93.46 | 92.36 | |
| ASR(%) | 100 | 33.05 | 98.23 | 23.61 | 8.67 | 73.85 | 7.81 | 99.94 | 0.01 | 6.89 | 1.58 | ||
| Trojan | ACC(%) | 93.81 | 91.78 | 92.18 | 94.16 | 93.28 | 84.85 | 78.45 | 80.11 | 93.00 | 93.60 | 92.40 | |
| ASR(%) | 100 | 99.91 | 99.97 | 1.12 | 1.71 | 3.12 | 4.04 | 6.22 | 1.23 | 2.36 | 2.19 | ||
| CL | ACC(%) | 93.82 | 92.51 | 91.53 | 93.48 | 93.66 | 84.15 | 86.59 | 84.58 | 91.17 | 93.3 | 92.26 | |
| ASR(%) | 99.66 | 99.73 | 0.98 | 1.46 | 0.87 | 99.98 | 21.47 | 99.93 | 99.97 | 0.87 | 1.37 | ||
| SIG | ACC(%) | 93.91 | 91.97 | 90.97 | 92.65 | 91.90 | 84.85 | 85.01 | 87.62 | 90.18 | 93.25 | 92.71 | |
| ASR(%) | 81.02 | 89.86 | 77.53 | 0.91 | 88.75 | 76.96 | 1.07 | 48.14 | 73.93 | 0.22 | 0.14 | ||
| Dynamic | ACC(%) | 94.43 | 91.71 | 92.13 | 92.98 | 93.65 | 88.64 | 86.84 | 90.05 | 92.03 | 94.03 | 92.47 | |
| ASR(%) | 99.85 | 8.48 | 16.76 | 17.01 | 4.46 | 15.64 | 22.67 | 99.95 | 2.39 | 7.17 | 6.28 | ||
| TaCT | ACC(%) | 94.23 | 92.26 | 92.76 | 92.86 | 93.91 | 81.33 | 85.65 | 92.75 | 92.97 | 94.23 | 92.66 | |
| ASR(%) | 97.48 | 72.68 | 97.45 | 0.96 | 0.48 | 87.9 | 9.75 | 2.82 | 68.71 | 2.51 | 2.17 | ||
| Adap -patch | ACC(%) | 93.86 | 92.02 | 91.12 | 93.6 | 93.08 | 77.03 | 85.54 | 89.16 | 93.46 | 93.55 | 92.56 | |
| ASR(%) | 99.68 | 92.17 | 99.06 | 1.15 | 95.16 | 99.96 | 6.12 | 2.23 | 10.52 | 1.04 | 1.49 | ||
| Adap -blend | ACC(%) | 93.95 | 91.65 | 91.68 | 93.9 | 93.31 | 93.87 | 87.63 | 80.57 | 92.18 | 93.8 | 92.68 | |
| ASR(%) | 94.74 | 10.87 | 94.51 | 96.13 | 5.39 | 80.67 | 22.65 | 9.13 | 0.68 | 0.48 | 1.47 | ||
| Average | ACC(%) | 93.97 | 92.15 | 91.77 | 93.42 | 93.33 | 85.38 | 85.27 | 86.25 | 92.33 | 93.67 | 92.45 | |
| ASR(%) | 96.93 | 56.38 | 65.02 | 23.64 | 22.93 | 70.89 | 10.82 | 41.14 | 39.71 | 2.46 | 1.99 | ||
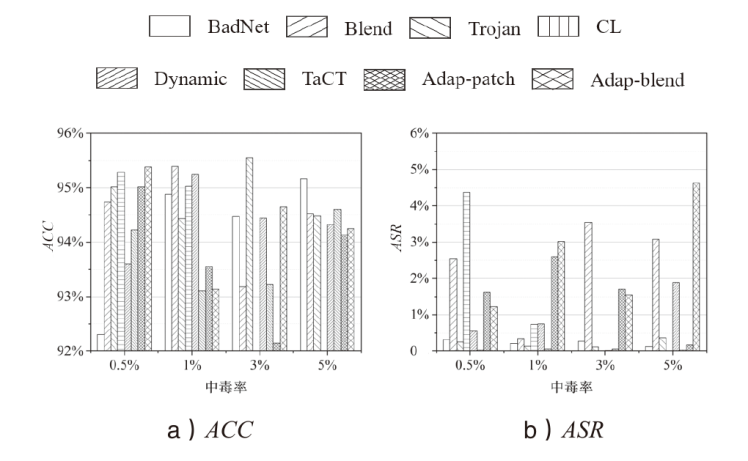
| G T S R B | BadNets | ACC(%) | 94.42 | 91.77 | 93.10 | 93.16 | 93.12 | 90.91 | 94.49 | 90.26 | 95.88 | 94.89 | 94.87 |
| ASR(%) | 94.88 | 0.62 | 0.56 | 0.88 | 13.56 | 17.63 | 6.05 | 0.08 | 100.00 | 0.26 | 0.21 | ||
| Blend | ACC(%) | 92.88 | 90.55 | 92.21 | 93.82 | 92.49 | 65.06 | 93.78 | 90.89 | 95.51 | 93.04 | 95.39 | |
| ASR(%) | 96.89 | 58.66 | 3.89 | 28.34 | 6.31 | 1.38 | 49.39 | 0.50 | 0.51 | 0.36 | 0.35 | ||
| Trojan | ACC(%) | 93.44 | 91.21 | 92.42 | 94.89 | 93.38 | 85.65 | 94.08 | 90.30 | 95.50 | 93.17 | 94.43 | |
| ASR(%) | 99.99 | 0.82 | 0.41 | 0.40 | 29.50 | 99.72 | 0.85 | 0.34 | 0.61 | 0.47 | 0.14 | ||
| SIG | ACC(%) | 93.23 | 88.94 | 90.44 | 93.19 | 93.23 | 82.41 | 93.64 | 91.80 | 96.18 | 93.10 | 95.02 | |
| ASR(%) | 49.39 | 28.36 | 53.12 | 4.15 | 49.39 | 38.29 | 6.38 | 20.78 | 21.36 | 0.92 | 0.74 | ||
| Dynamic | ACC(%) | 93.40 | 90.65 | 90.38 | 93.73 | 92.54 | 85.76 | 93.90 | 90.61 | 95.58 | 94.41 | 95.24 | |
| ASR(%) | 100.00 | 25.06 | 54.44 | 96.04 | 79.82 | 77.57 | 96.50 | 0.59 | 0.00 | 0.11 | 0.75 | ||
| TaCT | ACC(%) | 93.75 | 89.18 | 92.62 | 94.06 | 93.75 | 96.52 | 94.47 | 90.09 | 96.58 | 93.28 | 93.10 | |
| ASR(%) | 98.73 | 50.27 | 99.93 | 0.20 | 98.73 | 97.85 | 1.47 | 1.00 | 99.80 | 0.00 | 0.07 | ||
| Adap -patch | ACC(%) | 93.73 | 90.46 | 93.38 | 93.64 | 92.91 | 92.83 | 94.92 | 92.36 | 95.28 | 93.34 | 93.55 | |
| ASR(%) | 90.30 | 56.26 | 81.73 | 79.73 | 59.64 | 84.60 | 16.34 | 0.56 | 97.22 | 6.55 | 2.59 | ||
| Adap -blend | ACC(%) | 93.93 | 90.79 | 92.04 | 93.45 | 93.73 | 80.42 | 93.86 | 91.72 | 95.79 | 93.78 | 93.13 | |
| ASR(%) | 95.60 | 88.15 | 95.40 | 0.34 | 23.43 | 100.00 | 29.60 | 0.20 | 80.65 | 0.06 | 3.02 | ||
| Average | ACC(%) | 93.60 | 90.44 | 92.07 | 93.74 | 93.14 | 84.94 | 94.14 | 91.01 | 95.79 | 93.63 | 94.34 | |
| ASR(%) | 90.72 | 38.52 | 48.69 | 26.26 | 45.05 | 64.63 | 25.82 | 3.01 | 50.02 | 1.09 | 0.98 | ||
表5
RADAR消融实验结果与具体细节对比
| 第一次迭代 | 第二次迭代 | 第三次迭代 | TPR(%) | FPR(%) | ACC(%) | ASR(%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blend | |||||||||||||
| RADAR | 128/ 5000 | 2/ 495 | 4987/ 24270 | 15/ 12865 | 1/ 1283 | 4998/ 11608 | 2/ 19196 | 0/ 7674 | 4997/ 5020 | 99.94 | 0.05 | 92.36 | 2.33 |
| RADAR×w/o×SS | 952/ 500 | 95/ 495 | 2/ 30600 | 2514/ 9700 | 251/ 964 | 1/ 17136 | 2629/ 16432 | 1051/ 6566 | 3/ 3640 | 0.06 | 8.08 | 89.25 | 99.87 |
| RADAR×w/o×DP | 254/ 5000 | 2/ 495 | 4998/ 33144 | 2/ 8428 | 0/ 840 | 5000/ 18304 | 0/ 15848 | 0/ 6333 | 4997/ 5227 | 99.94 | 0.51 | 92.00 | 1.47 |
| RADAR×w× | 944/ 5000 | 94/ 495 | 17/ 9079 | 3508/ 20461 | 350/ 2041 | 2/ 6672 | 3049/ 21664 | 1219/ 8660 | 31/ 4293 | 0.62 | 9.47 | 87.83 | 99.95 |
| RADAR×w× | 128/ 5000 | 2/ 495 | 4998/ 32542 | 2/ 8729 | 0/ 868 | 4998/ 21598 | 2/ 14201 | 0/ 5675 | 4990/ 5241 | 99.80 | 0.56 | 91.94 | 2.61 |
| RADAR×w/o×Ad | 128/ 5000 | 2/ 495 | 4947/ 24270 | 17/ 12865 | 1/ 1283 | 5000/ 12020 | 0/ 18990 | 0/ 7591 | 4994/ 5168 | 99.88 | 0.39 | 91.91 | 2.43 |
| RADAR×w× 重新 训练 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 87.16 | 1.01 |
| Dynamic | |||||||||||||
| RADAR | 151/ 5000 | 0/ 495 | 5000/ 36601 | 0/ 6700 | 0/ 666 | 4996/ 22148 | 3/ 13926 | 1/ 5566 | 4997/ 5294 | 99.94 | 0.66 | 91.85 | 4.99 |
| RADAR×w/o×SS | 948/ 5000 | 93/ 495 | 923/ 11073 | 3167/ 19464 | 320/ 1941 | 360/ 7338 | 3113/ 21331 | 1245/ 8528 | 21/ 3934 | 0.42 | 8.69 | 88.53 | 99.97 |
| RADAR×w/o×DP | 178/ 5000 | 0/ 495 | 5000/ 38548 | 0/ 5726 | 0/ 570 | 4996/ 26346 | 4/ 11827 | 3/ 4730 | 4996/ 7043 | 99.92 | 4.54 | 91.08 | 9.64 |
| RADAR×w× | 188/ 5000 | 0/ 495 | 5000/ 36153 | 0/ 6924 | 0/ 688 | 4994/ 24699 | 6/ 12651 | 4/ 5050 | 4974/ 5203 | 99.48 | 0.51 | 93.46 | 85.77 |
| RADAR×w× | 151/ 5000 | 0/ 495 | 4977/ 36800 | 3/ 6600 | 0/ 654 | 5000/ 22963 | 0/ 13519 | 0/ 5407 | 4996/ 5596 | 99.92 | 1.33 | 92.90 | 9.73 |
| RADAR×w/o×Ad | 151/ 5000 | 0/ 495 | 5000/ 36601 | 0/ 6700 | 0/ 666 | 4996/ 23024 | 4/ 13488 | 1/ 5390 | 4996/ 5208 | 99.92 | 0.47 | 92.19 | 5.91 |
| RADAR×w× 重新 训练 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 88.43 | 4.97 |
| Adap-patch | |||||||||||||
| RADAR | 101/ 5000 | 1/ 495 | 4996/ 33467 | 4/ 8267 | 1/ 822 | 4983/ 22444 | 6/ 13778 | 1/ 5507 | 4962/ 5060 | 99.24 | 0.22 | 91.96 | 1.26 |
| RADAR×w/o×SS | 128/ 5000 | 4/ 495 | 4972/ 29324 | 21/ 10338 | 1/ 1029 | 4983/ 15758 | 15/ 17121 | 3/ 6843 | 4917/ 4985 | 98.34 | 0.15 | 92.12 | 2.18 |
| RADAR×w/o×DP | 107/ 5000 | 3/ 495 | 4991/ 32474 | 9/ 8763 | 3/ 873 | 4972/ 22794 | 17/ 13603 | 4/ 5441 | 4931/ 5151 | 99.42 | 0.48 | 91.13 | 2.62 |
| RADAR×w× | 126/ 5000 | 3/ 495 | 4942/ 21351 | 49/ 14325 | 4/ 1428 | 4936/ 13893 | 55/ 18054 | 23/ 7217 | 4857/ 4955 | 97.14 | 0.22 | 93.51 | 25.64 |
| RADAR×w× | 101/ 5000 | 1/ 495 | 4995/ 34788 | 5/ 7606 | 2/ 754 | 4993/ 23792 | 7/ 13104 | 4/ 5244 | 4930/ 5106 | 98.60 | 0.39 | 91.95 | 0.81 |
| RADAR×w/o×Ad | 101/ 5000 | 1/ 495 | 4995/ 33467 | 5/ 8267 | 1/ 822 | 4993/ 21409 | 7/ 14296 | 4/ 5714 | 4886/ 5715 | 97.72 | 1.84 | 91.9 | 11.10 |
| RADAR×w× 重新 训练 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 89.50 | 0.89 |
| Adap-blend | |||||||||||||
| RADAR | 87/ 5000 | 0/ 495 | 4985/ 25442 | 5/ 12279 | 1/ 1224 | 4989/ 12604 | 8/ 18698 | 2/ 7474 | 4972/ 5802 | 99.44 | 1.84 | 91.96 | 0.94 |
| RADAR×w/o×SS | 181/ 5000 | 7/ 495 | 4825/ 31713 | 63/ 9144 | 9/ 910 | 4954/ 13762 | 32/ 18119 | 12/ 7243 | 3018/ 3638 | 60.36 | 1.38 | 90.26 | 99.38 |
| RADAR×w/o×DP | 96/ 5000 | 4/ 495 | 4959/ 33326 | 10/ 8337 | 2/ 830 | 4986/ 18332 | 11/ 15834 | 5/ 6328 | 4891/ 5576 | 97.82 | 1.51 | 91.58 | 13.55 |
| RADAR×w× | 97/ 5000 | 0/ 495 | 4996/ 23759 | 2/ 13121 | 0/ 1307 | 4996/ 11741 | 1/ 19130 | 1/ 7646 | 4974/ 5575 | 99.48 | 1.33 | 93.51 | 0.43 |
| RADAR×w× | 87/ 5000 | 0/ 495 | 4983/ 28640 | 5/ 10680 | 1/ 1036 | 4979/ 14271 | 16 /17865 | 4/ 7144 | 4955/ 5407 | 99.10 | 1.01 | 92.15 | 1.86 |
| RADAR×w/o×Ad | 87/ 5000 | 0/ 495 | 4985/ 25442 | 5/ 12279 | 1/ 1224 | 4959/ 14558 | 31/ 17721 | 12/ 7082 | 4927/ 5510 | 98.54 | 1.29 | 91.73 | 5.56 |
| RADAR×w× 重新训练 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 87.51 | 3.64 |
| [1] | ZHANG Jinghuai, LIU Hongbin, JIA Jinyuan, et al. Data Poisoning Based Backdoor Attacks to Contrastive Learning[C]// IEEE. 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2024: 24357-24366. |
| [2] | HAN Xingshuo, WU Yutong, ZHANG Qingjie, et al. Backdooring Multimodal Learning[C]// IEEE. 2024 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy. New York: IEEE, 2024: 3385-3403. |
| [3] | XU Yuancheng, YAO Jiarui, SHU Manli, et al. Shadowcast: Stealthy Data Poisoning Attacks Against Vision-Language Models[C]// Neural Information Processing Systems. The 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: Curran Associates, 2024: 57733-57764. |
| [4] | GAO Mengnan, CHEN Wei, WU Lifa, et al. Survey on Backdoor Attacks and Defenses for Deep Learning Research[EB/OL]. (2025-04-27) [2025-04-29]. https://www.jos.org.cn/jos/article/pdf/7364. |
| 高梦楠, 陈伟, 吴礼发, 等. 面向深度学习的后门攻击及防御研究综述[EB/OL]. (2025-04-27) [2025-04-29]. https://www.jos.org.cn/jos/article/pdf/7364. | |
| [5] | WANG Renshuai, YANG Kuiwu, CHEN Yue, et al. Survey of Deep Learning Backdoor Attack on Image Data[EB/OL]. (2024-12-09) [2025-04-29]. https://www.ecice06.com/CN/10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.00%2070128. |
| 王人帅, 杨奎武, 陈越, 等. 面向图像数据的深度学习后门攻击技术综述[EB/OL]. (2024-12-09) [2025-04-29]. https://www.ecice06.com/CN/10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.00%2070128. | |
| [6] | ZHOU Jiachen, LYU Peizhuo, LAN Yibing, et al. DataElixir: Purifying Poisoned Dataset to Mitigate Backdoor Attacks via Diffusion Models[C]// AAAI. The 38th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Menlo Park: AAAI, 2024: 21850-21858. |
| [7] | AN Shengwei, CHOU S Y, ZHANG Kaiyuan, et al. Elijah: Eliminating Backdoors Injected in Diffusion Models via Distribution Shift[C]// AAAI. The 38th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Menlo Park: AAAI, 2024: 10847-10855. |
| [8] | ZHU Liuwan, NING Rui, LI Jiang, et al. Seer: Backdoor Detection for Vision-Language Models through Searching Target Text and Image Trigger Jointly[C]// AAAI. The 38th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Menlo Park: AAAI, 2024: 7766-7774. |
| [9] | BORGNIA E, GEIPING J, CHEREPANOVA V, et al. Dp-Instahide:Provably Defusing Poisoning and Backdoor Attacks with Differentially Private Data Augmentations[EB/OL]. (2021-05-21) [2025-04-29]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.02079. |
| [10] | TRAN B, LI J, MADRY A. Spectral Signatures in Backdoor Attacks[C]// Neural Information Processing Systems. The 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: Curran Associates, 2018: 8011-8021. |
| [11] | CHEN B, CARVALHO W, BARACALDO N, et al. Detecting Backdoor Attacks on Deep Neural Networks by Activation Clustering[EB/OL]. (2018-11-09) [2025-04-29]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1811.03728. |
| [12] | QI Xiangyu, XIE Tinghao, WANG J T, et al. Towards a Proactive ML Approach for Detecting Backdoor Poison Samples[C]// USENIX. 32nd USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security ’23). Berkeley: USENIX, 2023: 1685-1702. |
| [13] | DU Min, JIA Ruoxi, SONG D. Robust Anomaly Detection and Backdoor Attack Detection via Differential Privacy[EB/OL]. (2019-11-16) [2025-04-29]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1911.07116. |
| [14] | HONG S, CHANDRASEKARAN V, KAYA Y, et al. On the Effectiveness of Mitigating Data Poisoning Attacks with Gradient Shaping[EB/OL]. (2020-02-27) [2025-04-29]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2002.11497. |
| [15] | NGUYEN T D, RIEGER P, DE V R, et al. FLAME: Taming Backdoors in Federated Learning[C]// USENIX. 31st USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security ’22). Berkeley: USENIX, 2022: 1415-1432. |
| [16] | NASERI M, HAYES J, DE C E. Local and Central Differential Privacy for Robustness and Privacy in Federated Learning[EB/OL]. (2022-05-27) [2025-04-29]. https://www.ndss-symposium.org/wp-content/uploads/2022-54-paper.pdf. |
| [17] | LI Yige, LYU Xixiang, KOREN N, et al. Anti-Backdoor Learning: Training Clean Models on Poisoned Data[C]// Neural Information Processing Systems. The 35th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: Curran Associates, 2021: 14900-14912. |
| [18] | HUANG Kunzhe, LI Yiming, WU Baoyuan, et al. Backdoor Defense via Decoupling the Training Process[EB/OL]. (2022-02-05) [2025-04-29]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2202.03423. |
| [19] | ABADI M, CHU A, GOODFELLOW I, et al. Deep Learning with Differential Privacy[C]// ACM. The 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2016: 308-318. |
| [20] | LOWY A, LI Z, HUANG Tianjian, et al. Optimal Differentially Private Model Training with Public Data[EB/OL]. (2024-09-09) [2025-04-29]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.15056. |
| [21] | SHOKRI R, STRONATI M, SONG C, et al. Membership Inference Attacks Against Machine Learning Models[C]// IEEE. 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York: IEEE, 2017: 3-18. |
| [22] | ZHANG Zaixi, LIU Qi, HUANG Zhenya, et al. GraphMI: Extracting Private Graph Data from Graph Neural Networks[EB/OL]. (2021-06-05) [2025-04-29]. https://www.ijcai.org/proceedings/2021/0516.pdf. |
| [23] | ZHANG Shijie, YIN Hongzhi, CHEN Tong, et al. Graph Embedding for Recommendation Against Attribute Inference Attacks[C]// ACM. The Web Conference 2021. New York: ACM, 2021: 3002-3014. |
| [24] | NA S H, HONG H G, KIM J, et al. Closing the Loophole: Rethinking Reconstruction Attacks in Federated Learning from a Privacy Standpoint[C]// ACM. The 38th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference. New York: ACM, 2022: 332-345. |
| [25] | ZHU Heng, LING Qing. Bridging Differential Privacy and Byzantine-Robustness via Model Aggregation[EB/OL]. (2022-08-02) [2025-04-29]. https://www.ijcai.org/proceedings/2022/0337.pdf. |
| [26] | YAN Yukun, YE Qingqing, HU Haibo, et al. Towards Defending against Byzantine LDP Amplified Gain Attacks[EB/OL]. (2023-04-17) [2025-04-29]. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30637-2_42. |
| [27] | LECUYER M, ATLIDAKIS V, GEAMBASU R, et al. Certified Robustness to Adversarial Examples with Differential Privacy[C]// IEEE. IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York: IEEE, 2019: 656-672. |
| [28] | LIU Shijie, CULLEN A C, MONTAGUE P, et al. Enhancing the Antidote: Improved Pointwise Certifications Against Poisoning Attacks[C]// AAAI. The 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Menlo Park: AAAI, 2023: 8861-8869. |
| [29] | YAN Yukun, TANG Peng, CHEN Rui, et al. DPC:Filtering Out Patch-Based Poisoned Samples with Differential Privacy[EB/OL]. (2024-09-16) [2025-04-29]. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-70890-9_15. |
| [30] | KRIZHEVSKY A, HINTION G. Learning Multiple Layers of Features from Tiny Images[J]. Handbook of Systemic Autoimmune Diseases, 2009, 3: 1-7. |
| [31] | HOUBEN S, STALLKAMP J, SALMEN J, et al. Detection of Traffic Signs in Real-World Images: The German Traffic Sign Detection Benchmark[C]// IEEE. The 2013 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). New York: IEEE, 2013: 1-8. |
| [32] |
GU Tianyu, LIU Kang, DOLAN-GAVITT B, et al. Badnets: Evaluating Backdooring Attacks on Deep Neural Networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 47230-47244.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2909068 |
| [33] | CHEN Xinyun, LIU Chang, LI Bo, et al. Targeted Backdoor Attacks on Deep Learning Systems Using Data Poisoning[EB/OL]. (2017-12-15) [2025-04-29]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1712.05526. |
| [34] | LIU Yingqi, MA Shiqing, AAFER Y, et al. Trojaning Attack on Neural Networks[EB/OL]. (2017-09-05) [2025-04-29]. https://www.ndss-symposium.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/ndss2018_03A-5_Liu_paper.pdf. |
| [35] | TURNER A, TSIPRAS D, MADRY A. Label-Consistent Backdoor Attacks[EB/OL]. (2019-12-06) [2025-04-29]. https://www.arxiv.org/pdf/1912.02771. |
| [36] | BARNI M, KALLAS K, TONDI B. A New Backdoor Attack in CNNS by Training Set Corruption Without Label Poisoning[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). New York: IEEE, 2019: 101-105. |
| [37] | NGUYEN T A, TRAN A. Input-Aware Dynamic Backdoor Attack[C]// Neural Information Processing Systems. The 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: Curran Associates, 2020: 3454-3464. |
| [38] | QI Xiangyu, XIE Tinghao, LI Yiming, et al. Revisiting the Assumption of Latent Separability for Backdoor Defenses[EB/OL]. (2023-02-02) [2025-04-29]. https://openreview.net/pdf?id=_wSHsgrVali. |
| [39] | TANG Di, WANG Xiaofeng, TANG Haixu, et al. Demon in the Variant: Statistical Analysis of DNNs for Robust Backdoor Contamination Detection[C]// USENIX. 30th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security ’21). Berkeley: USENIX, 2021: 1541-1558. |
| [40] | WANG Bolun, YAO Yuanshun, SHAN S, et al. Neural Cleanse: Identifying and Mitigating Backdoor Attacks in Neural Networks[C]// IEEE. 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP). New York: IEEE, 2019: 707-723. |
| [41] | LI Yige, LYU Xixiang, KOREN N, et al. Neural Attention Distillation: Erasing Backdoor Triggers from Deep Neural Networks[EB/OL]. (2021-01-27) [2025-04-29]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2101.05930. |
| [42] | GAO Kuofeng, BAI Yang, GU Jindong, et al. Backdoor Defense via Adaptively Splitting Poisoned Dataset[C]// IEEE. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2023: 4005-4014. |
| [43] | MIRONOV I, TALWAR K, ZHANG Li. Rényi Differential Privacy of the Sampled Gaussian Mechanism[EB/OL]. (2021-01-27) [2025-04-29]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2101.05930. |
| [44] | ZENG Yi, PARK W, MAO Z M, et al. Rethinking the Backdoor Attacks’ Triggers: A Frequency Perspective[C]// IEEE. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. New York: IEEE, 2021: 16473-16481. |
| [45] | AL-KADER-HAMMOUD H A, BIBI A, TORR P H S, et al. Don't FREAK Out: A Frequency-Inspired Approach to Detecting Backdoor Poisoned Samples in DNNs[C]// IEEE. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2023: 2338-2345. |
| [46] | CHEN Ting, KORNBLITH S, NOROUZI M, et al. A Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning of Visual Representations[C]// IMLS. The 37th International Conference on Machine Learning. Brookline: JMLR, 2020: 1597-1607. |
| [47] | COHEN J, ROSENFELD E, KOLTER Z. Certified Adversarial Robustness via Randomized Smoothing[C]// IMLS. The 36th International Conference on Machine Learning. Brookline: JMLR, 2019: 1310-1320. |
| [48] | HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition[C]// IEEE. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2016: 770-77. |
| [1] | 赵锋, 范淞, 赵艳琦, 陈谦. 基于本地差分隐私的可穿戴医疗设备流数据隐私保护方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(5): 700-712. |
| [2] | 李骁, 宋晓, 李勇. 基于知识蒸馏的医疗诊断差分隐私方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(4): 524-535. |
| [3] | 徐茹枝, 仝雨蒙, 戴理朋. 基于异构数据的联邦学习自适应差分隐私方法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2025, 25(1): 63-77. |
| [4] | 夏辉, 钱祥运. 基于特征空间相似的隐形后门攻击[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(8): 1163-1172. |
| [5] | 尹春勇, 贾续康. 基于策略图的三维位置隐私发布算法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(4): 602-613. |
| [6] | 林怡航, 周鹏远, 吴治谦, 廖勇. 基于触发器逆向的联邦学习后门防御方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(2): 262-271. |
| [7] | 徐茹枝, 戴理朋, 夏迪娅, 杨鑫. 基于联邦学习的中心化差分隐私保护算法研究[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 69-79. |
| [8] | 尹春勇, 蒋奕阳. 基于个性化时空聚类的差分隐私轨迹保护模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2024, 24(1): 80-92. |
| [9] | 刘刚, 杨雯莉, 王同礼, 李阳. 基于云联邦的差分隐私保护动态推荐模型[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(7): 31-43. |
| [10] | 陈晶, 彭长根, 谭伟杰, 许德权. 基于差分隐私和秘密共享的多服务器联邦学习方案[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(7): 98-110. |
| [11] | 赵佳, 高塔, 张建成. 基于改进贝叶斯网络的高维数据本地差分隐私方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2023, 23(2): 19-25. |
| [12] | 刘峰, 杨成意, 於欣澄, 齐佳音. 面向去中心化双重差分隐私的谱图卷积神经网络[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(2): 39-46. |
| [13] | 晏燕, 张雄, 冯涛. 大数据统计划分发布的等比差分隐私预算分配方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2022, 22(11): 24-35. |
| [14] | 路宏琳, 王利明. 面向用户的支持用户掉线的联邦学习数据隐私保护方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2021, 21(3): 64-71. |
| [15] | 张佳程, 彭佳, 王雷. 大数据环境下的本地差分隐私图信息收集方法[J]. 信息网络安全, 2020, 20(6): 44-56. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||